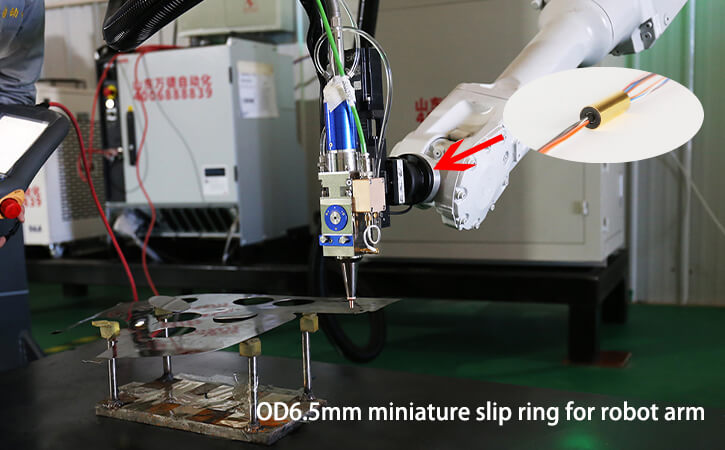
A hydraulic rotary union is an essential component in hydraulic systems, transferring hydraulic fluid from a stationary source to a rotating part. The rotary union allows for a rotating part to move and spin while still allowing the hydraulic fluid to pass through it, providing a useful tool for a variety of applications.
- What are Hydraulic Rotary Unions?
- Applications of Hydraulic Rotary Unions
- Advantages of Hydraulic Rotary Unions
- Conclusion
What are Hydraulic Rotary Unions?
Hydraulic rotary unions are devices specifically designed to transfer hydraulic fluid from a stationary source to a rotating piece of equipment such as a shaft or spindle. They are used in applications in which the hydraulic fluid must be kept isolated from other fluids, such as air and water, as well as from mechanical contamination.
Hydraulic rotary unions are typically made from metal and plastic components and are designed to be robust and reliable. The internal components of the device typically consist of two rotary union seals, a stationary seal, and a rotating seal, which allow the passage of the hydraulic fluid while keeping out other fluids or contaminants. The stationary seal is connected to the stationary source of the hydraulic fluid, and the rotating seal is connected to the rotating equipment.
The hydraulic rotary union also includes a bearing assembly that allows the rotating seal to remain in contact with the stationary seal while the equipment is rotating. This also prevents any damage to the Seals and allows the hydraulic fluid to be transferred smoothly and safely.
Hydraulic rotary unions are used in a variety of applications, including in industrial equipment, medical devices, and even the automotive industry. They are designed to handle a range of pressures and temperatures and are available in a variety of sizes, materials, and configurations.

Applications of Hydraulic Rotary Unions
Hydraulic rotary unions are critical components in many industrial applications where fluid needs to be transferred between stationary and rotating parts. Here are some detailed applications of hydraulic rotary unions across various industries:
Automotive Industry
- Testing Equipment: Used in dynamometers and test benches to transfer hydraulic fluid to simulate real-world conditions during the testing of engines, transmissions, and other automotive components.
- Manufacturing Robots: Integrated into robotic arms and automated assembly lines to supply hydraulic fluid for actuators and other moving parts.
Aerospace Industry
- Aircraft Component Testing: Essential for testing hydraulic systems in aircraft components, such as landing gear and control surfaces, ensuring they can withstand high pressures and rotational speeds.
- Flight Simulators: Used in the hydraulic systems of flight simulators to provide realistic movement and feedback.
Oil and Gas Industry
- Drilling Equipment: Employed in rotary drilling rigs to transfer hydraulic fluid to the drill head, enabling it to operate efficiently under high pressures and harsh conditions.
- Subsea Applications: Used in underwater exploration and production equipment to ensure reliable operation of hydraulic systems at great depths.
Manufacturing and Machine Tools
- CNC Machining Centers: Integrated into CNC machines to transfer coolant and lubrication fluids to the cutting tools, ensuring precision and efficiency.
- Hydraulic Presses: Used in hydraulic presses to transfer fluid to the press cylinders, enabling the application of high force for metal forming and other processes.
Renewable Energy
- Wind Turbines: Employed in the hydraulic pitch control systems of wind turbines to adjust the blade angles for optimal energy capture.
- Solar Trackers: Used in solar tracking systems to move and position solar panels for maximum sunlight exposure.
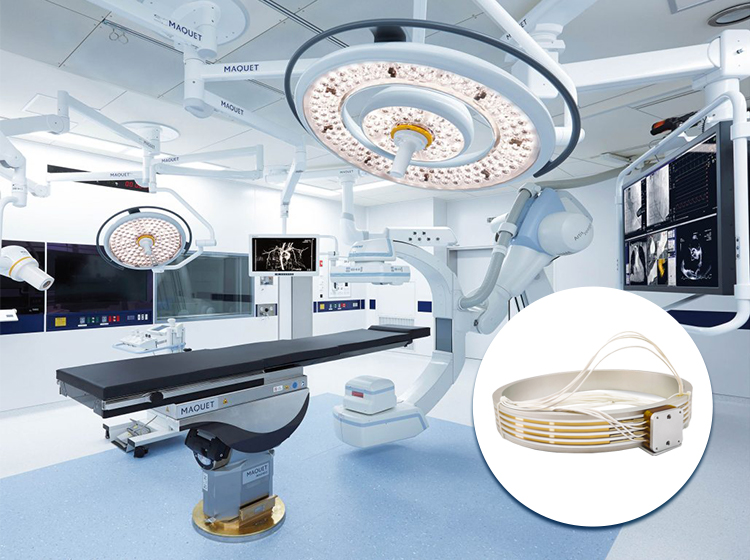
Medical Equipment
- MRI Machines: Integrated into MRI machines to transfer cooling fluids to the superconducting magnets, maintaining their operational temperature.
- Medical Robots: Used in medical robotic systems for precise fluid transfer to actuators and other components.
Food and Beverage Industry
- Packaging Machines: Utilized in packaging machines to transfer hydraulic fluid to the actuators, ensuring smooth and efficient packaging operations.
- Processing Equipment: Used in various food processing equipment to handle fluids in a hygienic and contamination-free manner.
Construction and Heavy Machinery
- Excavators and Cranes: Employed in the hydraulic systems of excavators, cranes, and other construction machinery to provide reliable fluid transfer for lifting and moving operations.
- Tunnel Boring Machines: Used in tunnel boring machines to transfer hydraulic fluid to the cutting heads and other rotating components.
Mining Industry
- Conveyors and Crushers: Integrated into the hydraulic systems of conveyors and crushers to transfer fluid for lubrication and actuation, ensuring smooth operation and reducing downtime.
- Drilling Rigs: Used in mining drilling rigs to transfer high-pressure hydraulic fluid to the drill heads.
Marine and Offshore Applications
- Deck Machinery: Employed in deck machinery such as winches and cranes to transfer hydraulic fluid, enabling the handling of heavy loads.
- Dynamic Positioning Systems: Used in the hydraulic systems of dynamic positioning systems to maintain the position of vessels and offshore platforms.
Hydraulic rotary unions are versatile components with applications across a wide range of industries. Their ability to transfer hydraulic fluid between stationary and rotating parts makes them essential for various mechanical systems. By providing reliable fluid transfer, they ensure the efficiency, precision, and longevity of the equipment in which they are used. When selecting a hydraulic rotary union, it is important to consider the specific requirements of the application, such as pressure, speed, and environmental conditions, to ensure optimal performance and durability.

Advantages of Hydraulic Rotary Unions
1. Improved Flow: They provide improved fluid flow compared to standard rotary joints because they are designed to reduce turbulence and increase the speed of fluid flow. This can result in increased productivity and efficiency in a variety of applications.
2. High Pressure: They are designed to handle high-pressure applications, making them a great choice for applications that require a reliable seal at high pressure.
3. Low Leakage: They are designed to reduce the amount of leakage, which can improve the overall efficiency of the system. This can reduce costs associated with replacing the lost fluid, as well as the costs associated with hazardous waste disposal.
4. Reliability: They are built to last and are designed to provide reliable performance. This ensures that the system will continue to operate at peak efficiency for an extended period of time.
5. Versatility: They are highly versatile and can be used in a variety of applications, from automotive to industrial. This makes them a great choice for a wide range of applications.
6. Cost-Effective: They are designed to be cost-effective, making them an economical choice for a variety of applications.
Hydraulic Rotary Unions Maximum RPM
Detailed Factors Affecting Maximum RPM
- Size and Design
- Small-sized Rotary Unions: These are generally designed for high-speed applications where space is limited. For example, a small-sized rotary union used in automotive testing equipment might handle up to 10,000 RPM due to its compact and precision-engineered components.
- Large-sized Rotary Unions: Larger unions used in heavy industrial machinery might be limited to lower RPMs, such as 200-500 RPM, due to the increased mass and inertia.
- Material
- Stainless Steel: Offers high strength and excellent wear resistance, suitable for high-speed applications. For instance, a stainless steel rotary union used in aerospace testing might achieve up to 5,000 RPM.
- Carbon Steel: Provides good strength but may be more suited for moderate speeds and general industrial use. These could handle RPMs up to 3,000.
- Special Alloys: Materials like titanium or specialized polymers can be used for very high-speed or specialized applications, potentially exceeding 10,000 RPM.
- Seal Type
- Lip Seals: Generally used for moderate speeds and pressures, typically handling RPMs up to 3,000.
- Mechanical Seals: More robust and can handle higher speeds and pressures, often used in high-speed applications. These might handle RPMs up to 10,000.
- O-Rings: Suitable for lower-speed applications, generally up to 1,000 RPM, depending on the material and application.
- Pressure and Temperature
- High Pressure: Rotary unions operating at high pressures (up to 10,000 PSI or more) might have reduced RPM ratings due to the increased stress on seals and bearings.
- High Temperature: High temperatures can degrade seal materials more quickly, often necessitating a reduction in maximum RPM to ensure longevity and safety. For instance, a rotary union operating at temperatures above 200°C might be limited to 1,500 RPM.
- Application-Specific Considerations
- Automotive Testing: Requires high RPMs for simulating real-world conditions. A hydraulic rotary union in this field might need to operate at speeds up to 12,000 RPM.
- Industrial Machinery: Often requires robust designs for durability rather than high speed. Here, a typical hydraulic rotary union might handle around 500-1,500 RPM.
- Aerospace: High precision and speed are crucial, so aerospace-grade hydraulic rotary unions might operate up to 8,000-10,000 RPM.
Examples of Specific Hydraulic Rotary Unions and Their Maximum RPM
- Deublin 1109 Series
- Material: Stainless steel
- Seal Type: Mechanical seals
- Max RPM: 5,000
- Applications: Machine tool spindles, automotive testing
- Rotoflux R Series
- Material: Carbon steel
- Seal Type: Lip seals
- Max RPM: 3,000
- Applications: General industrial machinery, packaging equipment
- Moog GAT Series
- Material: Special alloys
- Seal Type: High-performance lip seals
- Max RPM: 10,000
- Applications: High-speed spindles, aerospace testing
- DSTI HR Series
- Material: Stainless steel
- Seal Type: O-rings (high-temperature variant)
- Max RPM: 1,500
- Applications: High-temperature environments, oil and gas drilling
Hydraulic rotary unions are versatile components whose maximum RPM capabilities are influenced by various factors including size, material, seal type, operating pressure, temperature, and specific application requirements. Understanding these factors and consulting manufacturer specifications is crucial for selecting the appropriate rotary union for your needs.
For precise and detailed information, always refer to the specific product datasheets and technical support provided by the manufacturer, as they offer the most accurate and tailored information for each model.
Conclusion
A hydraulic rotary union is an essential component of hydraulic systems. They allow for precise control of hydraulic fluid flow, making them a useful tool for a variety of applications. Additionally, they are easy to install and maintain, making them a cost-effective option.
See What We Can Do