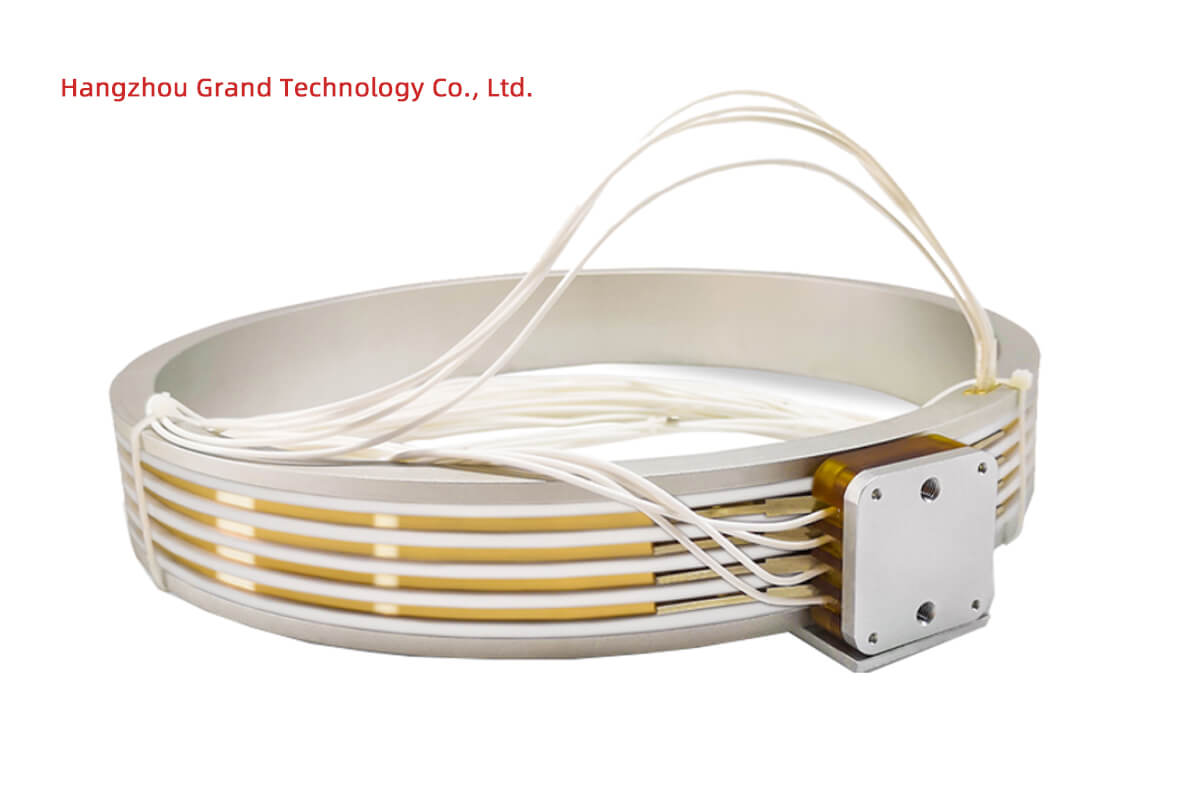
Signal slip rings, at first glance, might seem like minuscule components in the vast world of technology. However, their importance cannot be underestimated. In this introductory section, we will delve into the definition of signal slip rings and explore a high-level overview of their primary uses.
Definition of Signal Slip Rings
Signal slip rings are specialized electromechanical devices designed to transmit electrical power and data signals between stationary and rotating components. These devices typically consist of a rotating assembly with conductive rings and brushes that maintain a constant electrical connection during rotation. They eliminate the need for tangled cables and allow for continuous rotation while ensuring consistent, uninterrupted signal transmission.
Overview of Their Use
The versatile nature of signal slip rings enables their use in a wide range of applications, spanning from everyday gadgets to heavy-duty industrial equipment. Their key function is to allow for consistent signal transmission between stationary and moving parts. This capability is particularly important in devices or systems that rely on continuous rotation without signal disruption, such as wind turbines, satellite antennae, and security cameras.
In the subsequent sections of this guide, we will dive deeper into the core concept of signal slip rings, examine the different types available, and explore their various applications. As we move forward, we’ll address common concerns and misconceptions about signal slip rings, with the ultimate aim of providing you with a solid understanding of these essential but often underestimated components. So, let’s get started on our journey to appreciate the true importance and versatile nature of signal slip rings.
Basic Concept of Signal Slip Rings
The primary function of signal slip rings is to establish a continuous, undisrupted connection between fixed and rotating components, which is vital for the operations of many technological devices. It’s necessary to understand the fundamental concept behind this technology to fully appreciate its importance.
Explanation of What Signal Slip Rings Are
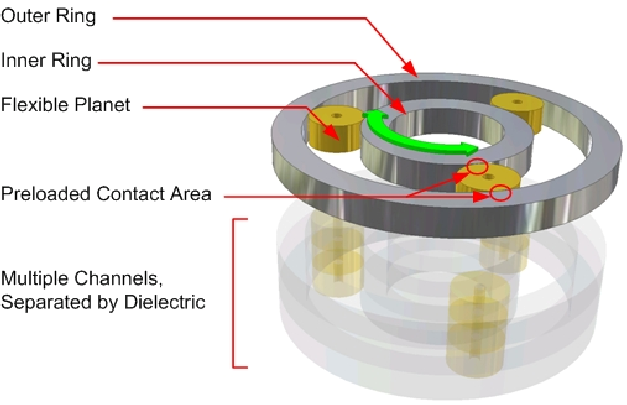
Signal slip rings, also referred to as rotary electrical interfaces, rotating electrical connectors, or electrical rotary joints, are devices designed to transfer electrical power and data signals from a stationary source to a rotating object. Made up of rings and brushes where the brushes slide over the rings creating an electrical connection, these devices prevent wires from tangling during the rotation, allowing for an uninterrupted signal transmission.
Basic Working Principles
The working principles of a signal slip ring revolve around electromechanical technology. The signal slip ring has two primary components: the stationary and rotary parts. The stationary part, also known as the stator, is connected to the input–power or data source, while the rotating part, referred to as the rotor, is linked to the component requiring power or data.
The electrical connection between the stationary and rotating parts is facilitated through rings and brushes. The brushes maintain contact with the rings, transmitting power or data despite the rotation. The number of rings and brushes corresponds to the number of circuits the signal slip ring can support.
Specification of Signal Slip Rings
The specification of signal slip rings can vary widely depending on the application and the specific requirements for signal transmission. Below are key specifications typically considered when selecting or designing a signal slip ring:
1. Number of Channels
- Description: The number of separate circuits or paths through which signals can be transmitted simultaneously.
- Typical Range: 2 to 50+ channels.
- Consideration: The number of channels needed depends on the complexity of the system and the number of signals that must be transmitted.
2. Signal Types
- Description: The types of signals the slip ring can transmit, such as analog, digital, RF (Radio Frequency), video, or data signals.
- Examples:
- Analog (e.g., sensor signals)
- Digital (e.g., data communication, control signals)
- High-frequency (e.g., Ethernet, USB)
- Consideration: Ensure the slip ring is compatible with the signal types in your application, especially if high-frequency or low-noise transmission is required.
3. Frequency Range
- Description: The frequency range within which the slip ring can effectively transmit signals.
- Typical Range:
- Low-frequency signals: 0-100 kHz
- High-frequency signals: 1 MHz to several GHz
- Consideration: Choose a slip ring with a frequency range that matches or exceeds the highest frequency of your signal.
4. Data Transmission Rate
- Description: The maximum rate at which data can be transmitted through the slip ring.
- Typical Range: Up to several Gbps (Gigabits per second) for high-speed data transmission.
- Consideration: Higher data rates are necessary for applications like HD video transmission or high-speed digital communication.
5. Electrical Noise
- Description: The level of electrical noise or interference introduced by the slip ring during signal transmission.
- Typical Range: Measured in millivolts (mV) or dB (decibels).
- Consideration: Low electrical noise is crucial for maintaining signal integrity, especially for sensitive or high-precision applications.
6. Contact Resistance
- Description: The resistance between the brush and ring contact points.
- Typical Range:
- Standard slip rings: 10-100 mΩ
- Low-resistance designs: <10 mΩ
- Consideration: Lower contact resistance is preferable as it reduces signal loss and improves transmission quality.
7. Dielectric Strength
- Description: The maximum voltage the slip ring can withstand without breakdown.
- Typical Range: 250 V to 1000 V (depending on the design and application).
- Consideration: Ensure the dielectric strength is sufficient to handle any voltage surges in the signal lines.

8. Operating Temperature Range
- Description: The range of ambient temperatures within which the slip ring can operate reliably.
- Typical Range: -40°C to +85°C, with extended ranges available for specialized environments.
- Consideration: Choose a slip ring that matches the environmental conditions of the application, especially for outdoor or high-temperature environments.
- Description: The maximum speed at which the slip ring can rotate while maintaining reliable signal transmission.
- Typical Range: 100 to 10,000 RPM (Revolutions Per Minute).
- Consideration: Higher rotational speeds may be necessary for applications like high-speed machinery or radar systems.
10. IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
- Description: The level of protection against dust and water ingress, rated by the IP (Ingress Protection) code.
- Typical Ratings:
- IP40 (basic protection)
- IP65 (dust-tight, protected against water jets)
- IP67 (dust-tight, protected against immersion)
- Consideration: Select an IP rating based on the environmental exposure of the slip ring. For outdoor or harsh environments, a higher IP rating is recommended.
11. Material and Finish
- Description: The materials used for the rings, brushes, and housing, which affect durability, corrosion resistance, and electrical performance.
- Common Materials:
- Rings: Gold, silver, or copper alloys
- Brushes: Precious metal alloys, carbon
- Housing: Aluminum, stainless steel, or plastic composites
- Consideration: Choose materials based on the required electrical performance and environmental durability.
12. Size and Form Factor
- Description: The physical dimensions of the slip ring, including outer diameter, length, and mounting configuration.
- Typical Range: Varies widely based on application; miniaturized slip rings are available for compact systems.
- Consideration: Ensure the slip ring fits within the spatial constraints of your system design.
13. Connector Type
- Description: The type of connectors used for interfacing with the signal slip ring.
- Common Types:
- Wires with terminals
- PCB connectors
- Customized connector interfaces
- Consideration: Select a connector type that is compatible with your system’s wiring and ease of installation.
14. Vibration and Shock Resistance
- Description: The slip ring’s ability to withstand mechanical vibrations and shocks without affecting performance.
- Typical Range: Vibration up to 10 G, shock up to 50 G (application-specific).
- Consideration: Essential for applications in aerospace, defense, and heavy industrial machinery.
These specifications should be carefully evaluated when selecting a signal slip ring to ensure it meets the specific needs of your application, from signal integrity and reliability to durability and environmental compatibility.
Different Types of Signal Slip Rings
Just as there is a wide variety of applications for signal slip rings, there exists considerable diversity in the types of signal slip rings themselves. They can vary in terms of size, design, lifespan, and operation, depending on specific industry requirements. By analyzing their construction material, the number of circuits, and the types of signals they can transmit, we can further classify these critical devices.
Classification Based on Materials Used in Construction
Based on construction materials, signal slip rings can be typically categorized into two types: Metal Contact Slip Rings and Fiber Optic Slip Rings.
Metal Contact Slip Rings
These are the most common type of slip rings and comprise metal components. They are typically less expensive and simpler in design, transmitting power and data through sliding contact between brushes and rings. The common metals used are gold, silver, copper, and alloys which determine the durability, conduction efficiency, and cost.
Fiber Optic Slip Rings (FORJs)
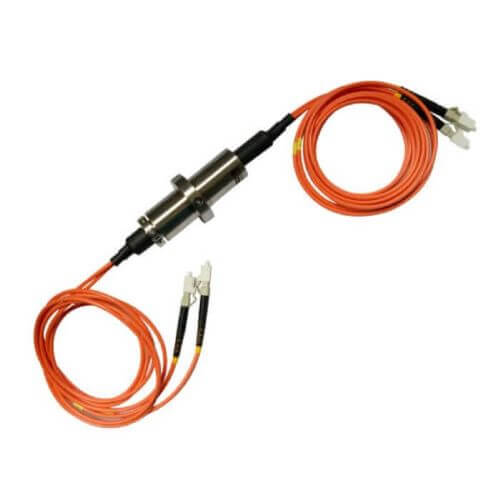

These use optical fibers instead of metal to transmit signals. FORJs offer higher data transmission rates and cater to high-performance applications where radio frequency interference is a concern. They are more expensive than metal contact slip rings due to their complexity and superior data transmission benefits.
Classification Based on Number of Circuits
Signal slip rings can be designed with any number of circuits to meet unique application needs.
Single-Channel Slip Rings
These slip rings have one circuit and are often used in simple or less demanding applications such as miniature electric devices.
Multi-Channel Slip Rings
These types can handle numerous circuits, allowing for the simultaneous transmission of power and various data signals. They are employed in complex applications like medical imaging devices, massive industrial machinery, or satellite communication systems.
Classification Based on Signal Types They Can Transmit
The classification can also be based on the type of signals the slip rings are designed to transmit:
Power Signal Slip Rings
These variants are primarily designed to transmit power from a stationary source to a rotating assembly.
Data Signal Slip Rings
These are used to transmit data signals including Ethernet, HDMI, USB, CAN Bus or other types of data signals between stationary and moving parts.
Hybrid Slip Rings
These slip rings are capable of transmitting both power and data signals and are used in complex systems where both types of signals are required.
Understanding the diversity and specific features of different signal slip rings will equip you to make more informed decisions when choosing the appropriate device for your specific needs, as discussed in future sections.
Power and Signal Slip Rings
Power and signal slip rings are crucial components in various rotating systems, enabling the seamless transmission of electrical power and signals from a stationary structure to a rotating one. These devices are commonly used in applications where continuous rotation is required, such as in wind turbines, medical devices, robotics, and other industrial machinery.
Components and Structure
A typical power and signal slip ring consists of the following parts:
- Rotor: The rotating part of the slip ring, connected to the rotating component of the system.
- Stator: The stationary part of the slip ring, connected to the fixed part of the system.
- Conductive Rings: These are circular metal rings attached to the rotor. They rotate along with the rotor and provide paths for electrical currents.
- Brushes: Fixed conductive elements attached to the stator. They maintain constant contact with the rotating rings, allowing electrical currents to pass between the stationary and rotating components.
- Housing: The outer casing that protects the internal components from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and mechanical damage.
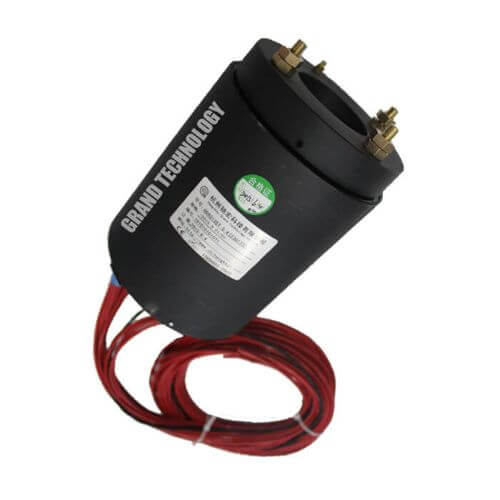

Types of Power and Signal Slip Rings
- Power Slip Rings: These are designed to transmit high power, typically for driving motors, generators, or other high-power devices. They are capable of handling high currents and voltages.
- Signal Slip Rings: These are designed to transmit data signals, including analog and digital signals. They are used in applications requiring reliable communication, such as in data acquisition systems, sensors, and control systems.
- Hybrid Slip Rings: These combine the functionality of power and signal slip rings, allowing both power and data to be transmitted through a single slip ring unit. Hybrid slip rings are often used in complex systems, such as advanced robotic arms, where both power and control signals are needed.
Applications
- Wind Turbines: Slip rings in wind turbines allow the transfer of electrical power from the rotating blades to the stationary grid connection, as well as the transmission of control signals for blade pitch adjustment.
- Medical Imaging Equipment: In MRI and CT scanners, slip rings enable the continuous rotation of imaging components while transmitting power and high-definition data signals.
- Robotics: Slip rings are used in robotic arms and other automated machinery to provide power and control signals to the rotating joints, allowing for smooth and continuous operation.
- Radar Systems: Slip rings in radar systems facilitate the transfer of power and data between the rotating antenna and the stationary base, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
- Aerospace and Defense: Slip rings are used in various aerospace and defense applications, including gyroscopes, surveillance systems, and satellite communication, where reliable power and signal transmission is critical.
Advantages
- Continuous Rotation: Slip rings allow for 360-degree rotation without the risk of cable tangling or mechanical stress.
- Compact and Integrated Design: They provide a compact solution for transmitting multiple channels of power and signals through a single unit, simplifying system design and reducing space requirements.
- High Reliability and Durability: Modern slip rings are designed for high durability, capable of withstanding harsh operating conditions while requiring minimal maintenance.
- Versatility: Slip rings can be customized to meet specific application requirements, including different power ratings, signal types, and environmental conditions.
Considerations for Selection
- Current and Voltage Ratings: Ensure the slip ring is rated for the required power levels, considering both peak and continuous currents.
- Signal Integrity: For signal slip rings, consider the types of signals being transmitted (analog, digital, high-frequency) and ensure the slip ring is designed to minimize noise and signal degradation.
- Environmental Conditions: Choose slip rings with appropriate sealing and protection if they will be exposed to harsh environments, such as extreme temperatures, moisture, or dust.
- Wear and Maintenance: Consider the expected wear of the slip ring, particularly in high-speed or high-duty-cycle applications. Some slip rings use advanced materials to reduce wear and extend service life.
- Size and Form Factor: Ensure the slip ring fits within the spatial constraints of your application, considering both the diameter and length of the unit.
Power and signal slip rings are vital components in many modern rotating systems, providing a reliable and efficient means to transfer power and data without the limitations of fixed wiring. Their ability to support continuous rotation makes them indispensable in a wide range of industrial, medical, and technological applications.
Capacitive Signal Slip Rings
Capacitive signal slip rings are a specialized type of slip rings designed to transmit signals using capacitive coupling rather than direct electrical contact, as in traditional slip rings. This technology is particularly useful for applications that require high-frequency signal transmission, reduced wear and tear, and minimal electrical noise.
How Capacitive Signal Slip Rings Work
Capacitive signal slip rings utilize the principle of capacitive coupling to transmit electrical signals between stationary and rotating parts. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Capacitive Plates: Instead of using conductive rings and brushes, capacitive slip rings use pairs of capacitive plates. These plates are positioned near each other—one set on the rotating component (rotor) and the other on the stationary component (stator).
- Signal Transmission: When a signal is applied to one of the capacitive plates, it generates an electric field. This field induces a corresponding signal in the opposite plate due to capacitive coupling. The signal is then transmitted from the rotor to the stator without any direct electrical contact.
- Non-Contact Operation: Since the transmission is achieved through the electric field and not through physical contact, there is no friction or wear between the components. This results in a longer lifespan and less maintenance compared to traditional slip rings.
Advantages of Capacitive Signal Slip Rings
- High-Frequency Capability: Capacitive coupling is particularly well-suited for transmitting high-frequency signals, making these slip rings ideal for applications like high-speed data transmission and high-resolution video signals.
- Minimal Electrical Noise: Traditional slip rings can introduce electrical noise due to the friction between brushes and rings. Capacitive slip rings, with their non-contact design, significantly reduce this noise, leading to clearer signal transmission.
- Low Wear and Maintenance: The absence of direct physical contact between moving parts reduces wear and tear, leading to longer operational life and lower maintenance requirements.
- Compact Design: Capacitive slip rings can be designed to be very compact, making them suitable for applications where space is a constraint.
- High Reliability: The reduced wear and lower electrical noise result in a more reliable operation, which is critical in precision applications.
Applications of Capacitive Signal Slip Rings
- Medical Imaging: In devices like MRI and CT scanners, capacitive slip rings are used to transmit high-resolution images with minimal noise while allowing continuous rotation of the imaging components.
- High-Speed Data Transmission: Capacitive slip rings are ideal for transmitting data in applications that require high-speed communication, such as in advanced robotics, aerospace systems, and satellite communications.
- Rotary Sensors: Used in applications like rotary encoders and sensors, where accurate, low-noise signal transmission is essential for precise measurements.
- Surveillance Systems: In rotating camera systems, capacitive slip rings allow the transmission of high-definition video signals without introducing noise or signal degradation.
- Wind Turbines: In some advanced wind turbine designs, capacitive slip rings are used to transmit control signals for blade pitch adjustments while minimizing maintenance needs.
Considerations
- Signal Attenuation: While capacitive slip rings are excellent for high-frequency signals, they may not be suitable for low-frequency or power transmission applications due to potential signal attenuation.
- Cost: Capacitive slip rings can be more expensive than traditional slip rings, especially when high-precision manufacturing is required.
- Environmental Factors: Like other electronic components, capacitive slip rings may be sensitive to environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, and electromagnetic interference. Proper shielding and environmental controls may be necessary in harsh conditions.
Capacitive signal slip rings offer a high-performance, low-maintenance solution for transmitting signals in rotating systems, particularly where high-frequency, low-noise transmission is required.
Applications of Signal Slip Rings
Signal slip rings boast a myriad of applications across diverse industries and sectors. The following sections delve into the breadth of industries that harness their functions, their critical role in numerous machines, and tangible real-world examples of their deployment.
Industries and Sectors Where Signal Slip Rings Are Used
The universal presence of signal slip rings across sectors is a testament to their pivotal role. From medicine to manufacturing, energy to entertainment, they facilitate smooth operations in both rotating and stationary components.
- Renewable Energy: Crucial to wind turbines and solar panels, signal slip rings transfer data and power to keep the blades rotating and panels tracking the sun.

- Manufacturing: From assembly lines to machines that require rotation, these devices are ubiquitous in industrial settings, ensuring uninterrupted operations.
- Medical: In advanced imaging devices like MRI and CT scanners, signal slip rings help transmit high-resolution image data to stationary monitors.

- Military & Defense: They facilitate signals and data transfer in radar systems, weapon rotary turrets, and military-grade robotics.

- Aerospace: Signal slip rings are employed in satellite systems, transmitting critical data between the Earth and the rotating satellite.
Role of Signal Slip Rings in Different Machines and Devices
Signal slip rings bring technological designs to life, allowing for rotational motion while maintaining an uninterrupted electrical connection. These devices are critical components that seamlessly handle power transmission or data signals.
In machines with rotating parts, like wind turbines, signal slip rings deliver electrical power from the stationary part to the moving parts, facilitating uninterrupted rotation. In data-driven applications, such as CT scanners, they transmit the image data from the rotating scanner to the stationary display.
Real-World Examples of Signal Slip Ring Applications
Wind Turbines: Wind turbines capture the kinetic energy of the wind and convert it into electricity. For the turbines to follow the wind direction for maximum efficiency, they have to rotate continuously. Signal slip rings facilitate this continuous rotation of the entire structure without disruption in power or signal transmission.
CCTV Cameras: Security cameras that need to rotate 360 degrees to monitor a large area use signal slip rings to ensure the data from the rotating camera can be transmitted to the stationary recording or monitoring system without getting wires twisted or signals disrupted.
MRI Scanners: In an MRI scanner, the patient is surrounded by a large, rotating magnetic field. Signal slip rings in these machines ensure that high-quality imaging data is transmitted from the rotating part to the stationary computer system, allowing doctors to analyze and diagnose medical conditions.
By understanding the broad scope of industries and machines where signal slip rings come into play, and by bringing the discussion to life with tangible real-world examples, we deepen our appreciation for these unassuming, yet fundamental devices.
Common Concerns and Misconceptions about Signal Slip Rings
While signal slip rings are indispensable pieces of technology, they are also prone to certain concerns and misconceptions. By identifying potential sources of failure, learning how to detect issues and prevent them before they arise, and debunking prevalent misconceptions, we can better manage these essential devices.
Common Sources of Failure or Malfunction
Wear and Tear: Being mechanical devices, slip rings are subject to wear and tear over time. The constant sliding action between the brushes and the rings results in gradual degradation, eventually impacting the device’s functionality.
Poor Maintenance: Irregular or inadequate maintenance often leads to failures. Regular cleaning and inspection can prevent particle build-up that could cause an electrical short or affect the brush-rings connection.
Environmental Factors: Harsh environments or exposure to extreme temperatures, high humidity, dust, or corrosive materials can compromise the performance and lifespan of slip rings.
How to Detect Issues with Your Signal Slip Ring
Changes in Output: Anomalies in the data output, sporadic signals, or variations in power output may be indicative of issues with the slip ring.
Visual Inspection: Regular visual assessments are beneficial. Unusual wear patterns, particle build-up, or discoloration could suggest problems.
Noise and Vibration: Excessive noise or vibration during operation can also be a sign of possible issues, like misalignment or wear.
How to Prevent Problems Before They Arise
Regular Maintenance: Routinely cleaning and inspecting your slip rings can prevent many mechanical issues. This includes checking for wear, ensuring correct alignment, and cleaning brushes and rings.
Appropriate Sizing and Installation: Ensuring that the slip ring is appropriate for the application’s load requirements and is correctly installed can minimise the chances of early failure.
Protection from Harsh Conditions: If the slip ring operates in a harsh environment, protective measures like sealing or encapsulation are recommended to extend the lifespan.
Debunking Misconceptions about Signal Slip Rings
Misconception 1 – “All slip rings are the same:” Slip rings vary greatly – from the number of circuits they can handle, the type of signals they transmit, to their size and construction material.
Misconception 2 – “Slip rings require no maintenance:” Regular maintenance is essential for the longevity and performance of slip rings, regardless of the construction type or quality.
Misconception 3 – “Slip rings can be used in any environment:” Not all slip rings are designed for harsh environments. Factors like humidity, temperature, and dust can significantly impact their longevity and performance.

A good understanding of these common concerns, detection methods, preventive measures, and misconceptions paves the way for more effective use and management of signal slip rings.
Choosing the Right Signal Slip Ring for Your Application
Selecting the correct signal slip ring demands a deep understanding of your application’s specific needs, a mindful assessment of various models, and an awareness of pertinent purchasing considerations. This section aims to guide you on vital considerations, and differences among brands and provides a checklist for prospective buyers.
What to Consider When Purchasing
Signal Quality: Your choice must reliably handle the types of signals typical for your application, whether it’s power, data, or a hybrid of the two. Quality of transmission and the bandwidth needed are vital considerations.
Noise: Mechanical and electrical noise affects the reliability of the signals transmitted. A slip ring with low noise levels is more reliable and ensures accurate data exchange and power transmission.
Maintenance: Consider how easy it is to maintain the slip ring – some designs are easily accessible and simple to clean, which can reduce long-term maintenance costs.
Lifespan: Consider the expected lifespan of the slip ring, keeping in mind that higher levels of durability often warrant higher upfront costs.
Comparison of Different Brands/Models
Comparing different slip ring models and manufacturers can help you determine the most suitable option. Analyze based on:
Price: Different brands offer varying prices. Don’t necessarily opt for the cheapest option – ensure it meets your needs and is of good quality.
Quality: Do the brands/models have a reputation for quality and reliability?
Technical Support: Check if the manufacturer offers comprehensive support services – this can be beneficial if you face issues or require replacement parts.
Reviews: Look at reviews and feedback about the brand/model. Are existing users generally satisfied?
Checklist for Buyers
When purchasing a signal slip ring, this checklist might be helpful:
- Understand Your Needs: Identify the types of signals (data or power) you need to transmit, the number of circuits required, and the environmental conditions.
- Assess Specifications: Examine the bandwidth, rotational speed, noise levels, and overall signal integrity.
- Price vs Quality: Strike a balance between price and quality. Aim for a device that matches your budget but doesn’t compromise on quality.
- Maintenance and Lifespan: Identify the expected lifespan and necessary maintenance schedule.
- Manufacturer Support: Ascertain if the manufacturer offers solid support services and a good warranty.
Making the correct choice of signal slip ring isn’t only about understanding the device but also about intimate knowledge of your application’s needs and a careful comparison of the available options on the market. Armed with this knowledge, you are better positioned to make an informed decision.
Installation and Maintenance of Signal Slip Rings
Once you have the appropriate signal slip ring for your application, successful installation and maintenance are paramount. The following sections provide a step-by-step guide on installation, offer maintenance tips to extend the device’s lifespan, help troubleshoot common issues, and outline safety considerations.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Install Signal Slip Rings
- Understand the Assembly Diagram: Before starting the installation, thoroughly understand the assembly diagram provided by the manufacturer.
- Prepare the Site: Ensure the slip ring’s mounting space is clean, dry, and free from potential obstructions.
- Install the Slip Ring: Once the area is prepared, secure the slip ring as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Make sure the device is properly aligned and fastened to prevent instability or vibration during operation.
- Connect the Wires: Next, connect the wires to the associated rotating and stationary components as advised in the instruction manual. Double-check all connections to ensure accuracy.
- Test the Connection: After installation, run a test to ensure the slip ring is operating correctly. Reconfirm signal continuity and integrity.
Maintenance Tips to Extend Lifespan
- Regular Cleaning: Gently clean and remove any dust or foreign particles to prevent blockages or friction which can affect the electric current flow.
- Periodic Inspection: Regularly inspect the slip ring for signs of wear or damage. Pay particular attention to the brushes and the ring’s surface.
- Proper Lubrication: Ensure that the slip ring is well-lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
Trouble-Shooting Common Issues
- Inconsistent Signal: If the output signal is inconsistent or intermittent, check for proper connections, signs of wear on the rings and brushes, or loose parts.
- Increased Noise or Vibration: This could indicate misalignment during assembly or excessive wear. Realignment or part replacement may be necessary.
- Failure to Operate: In case of total cessation, verify the part’s conduction paths, and ensure that the device is correctly connected and there hasn’t been an electrical short circuit.
Safety Considerations
- Turn off Power: Always turn off power during installation or maintenance to mitigate the risk of electrical shocks.
- Use Proper Tools: Always use the right, non-conductive tools for installation and maintenance to avoid accidental short circuits.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Adhering to the guidelines provided by the manufacturer ensures the proper handling of the device.
Whether you are in the initial stages of installing a signal slip ring, maintaining your device to ensure long-term efficacy, or troubleshooting common issues, these steps should help you foster a seamless and safe experience with your device.
The Future of Signal Slip Rings
As technology advances, the need for efficient and reliable data and power transmission solutions will continue to grow. The future of signal slip rings promises new innovations, changes in their utilization, and the expansion of their applications.
Upcoming Technological Advancements
- Higher Bandwidth and Data Rate Transmission: Slip rings will need to support increasingly higher data rates and bandwidth requirements, driving advancements in materials, design, and conductive solutions.
- Improved Materials: New and advanced materials, coatings, and contact technologies will minimize issues like wear, friction, and electrical noise, resulting in slip rings with longer service life and better overall performance.
- Integration with Advanced Sensing Technologies: Slip rings may incorporate smart sensors for monitoring real-time performance parameters, such as brush wear, temperature, and lubrication conditions. These advancements will streamline maintenance processes and enable predictive maintenance schedules.
- Compact and Lightweight Designs: Technological advancements will drive the development of smaller, lighter-weight slip rings that can be effectively incorporated into a wider array of applications.
Predicted Changes in How Signal Slip Rings Are Used
- Simplified Maintenance: Advanced sensing technologies and new materials will make maintaining slip rings easier, reducing overall costs and downtime.
- Increased Adoption of Renewable Energy: As renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, become more widespread, slip rings will play a crucial role in these systems to ensure efficient energy transmission.
- Expansion into New Industries: Emerging industries, like UAV systems, robotics, and electromobility, will continue to integrate slip rings into their designs.
Potential New Applications for Signal Slip Rings
- Space Applications: As space exploration evolves, slip rings will play a critical role in satellite and spacecraft systems, providing vital power and data transmission links in these harsh environments.
- Underwater Systems: Slip rings are likely to find increased use in oceanic applications, such as subsea exploration, ROVs, and submersible equipment.
- Biomedical Devices: The medical industry will potentially integrate slip rings into advanced diagnostic systems, robotic surgery tools, or MRI machines, which require reliable signal transmission between moving components.
The future of signal slip rings holds exciting opportunities, driven by technological advancements and an increasing demand for efficient power and data transfer solutions. Embracing new innovations and applications will shape the industry for years to come.
Conclusion
Signal slip rings play a vital role in various industries, enabling the efficient and reliable transfer of power and data between stationary and rotating components. With applications spanning robotics, aviation, communications, and renewable energy, their importance cannot be overstated.
To fully benefit from these devices, it is crucial to make the proper selection, considering factors such as signal quality, noise, maintenance, and lifespan. Research and assessments of different models and brands allow for a more informed choice that meets the specific needs of your application.
Furthermore, understanding and carrying out correct installation, regular maintenance, and addressing any issues in a timely manner ensures long-lasting and satisfactory performance of the signal slip ring.
Get a detailed quote for signal slip rings tailored to your application.
In conclusion, signal slip rings are indispensable in modern applications where reliable rotary electrical connections are required. By focusing on proper selection, use, and maintenance, you can maximize the value and longevity of these devices, thus ensuring the success of your projects.
FAQs about Signal Slip Rings
Q: How durable are signal slip rings, and how long can I expect them to last, especially in harsh operational conditions?
A: The durability and lifespan of signal slip rings greatly depend on the quality of materials, the design, and the application environment. Choose a model specifically designed for harsh conditions if necessary, and ensure proper maintenance to extend its service life. Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for expected lifespan and usage conditions.
Q: Does paying more for a signal slip ring guarantee better quality and durability?
A: While higher-priced slip rings may offer better materials, design, and performance, it is not a universal rule. Carefully assess the specifications and reviews of various models within your budget to strike a balance between price and quality.
Q: How often do signal slip rings need maintenance, and can I perform maintenance tasks myself?
A: Maintenance requirements vary depending on the slip ring type, design, and operating conditions. Typically, regular cleaning and inspections are necessary to ensure optimal performance. Most basic maintenance tasks, like cleaning and lubrication, can often be performed by users. However, always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific guidance.
Q: How can I maintain a clean, uninterrupted signal when using a signal slip ring?
A: To maintain signal integrity, choose a slip ring with specifications that match your application’s requirements, such as bandwidth and noise levels. Proper installation, alignment, and regular maintenance also contribute to maintaining a clean signal.
Q: Is the installation process for signal slip rings complicated?
A: The complexity of installing a signal slip ring depends on the specific device and application. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for step-by-step guidance. If you are unsure, it is recommended to consult with a professional or contact the manufacturer for assistance.
Q: How can I determine if a new slip ring is compatible with my current system when replacing an existing one?
A: To ensure compatibility, carefully review the new slip ring’s specifications and dimensions, verify the number of circuits, and confirm its ability to handle the required signal types (power or data). Consult the manufacturer or a professional for guidance to ensure a suitable match between the new slip ring and your current system.


