Electromechanical systems include an array of components, each playing a distinct role in the seamless functioning of the entire setup. Among these, the slip ring collector, also known simply as a slip ring, is a pivotal device that often goes unnoticed due to its mundane appearance and compact size. Despite its understated presence, a slip ring collector carries out a key task in many machinery and systems that involve a rotating interface.
The primary function of a slip ring collector stems from its unique capability to transmit electrical signals and power smoothly and effectively from a stationary part of a system to a rotating part, or vice versa. This seemingly simple task is, in fact, a critical operation. For example, imagine the blades in a wind turbine that continuously rotate, generating power that needs to be transferred from the dynamic, moving parts to the stationary base for further processing and distribution. A slip ring collector perfectly facilitates this power transfer, bridging the rotating components with the fixed ones.
Moreover, a slip ring collector plays a crucial role in transferring not just power but also signals. An evident example can be observed in medical imaging devices or surveillance systems where the device needs to rotate fully or partially while continuously transmitting electrical signals. In these applications, the slip ring collector ensures that the signals, which could carry critical real-time data, are reliably transferred from the moving parts to the stationary ones without any disruption. Without the slip ring’s facilitation, the constant signal interventions due to the rotation could lead to incorrect or incomplete data.
Thus, in the broader context of electromechanical systems, the slip ring collector is not a mere afterthought but rather a vital component, a silent enabler whose performance can be a deciding factor in the overall efficiency and effectiveness of many machines and systems.
Types of Slip Ring Collectors
Just as there is a wide variety of applications for slip ring collectors, numerous types are also available, each designed with specific characteristics to serve particular needs. Here, we delve into the details of some of the most commonly used types:
Capsule Slip Rings
As the name suggests, capsule slip rings sport a compact design, akin to a capsule. Despite their small form factor, they are versatile and able to transmit a mix of signals and power. Specifically designed to cope with limited space applications, these are perfect for situations where space-saving is of paramount concern without compromising the signal or power transfer quality.
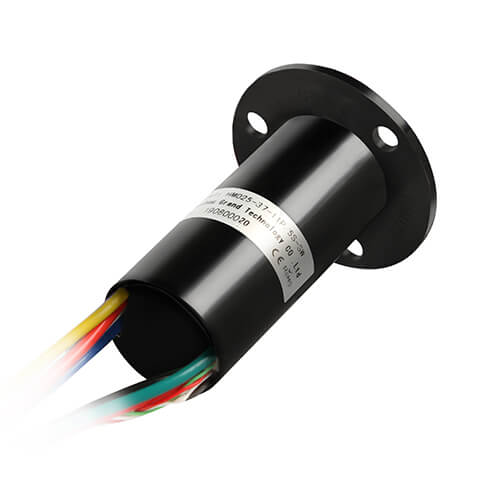

Through-Bore Slip Rings
Sliding into view next, are the through-bore slip rings. Unique in their form, these slip rings feature a hollow shaft in their center. This ‘bore’ or ‘hole’ provides an avenue for routing cables or mounting the slip ring around a shaft. This type is commonly used in scenarios where there are medium to high circuit counts and where the system requires a center hole for other components.
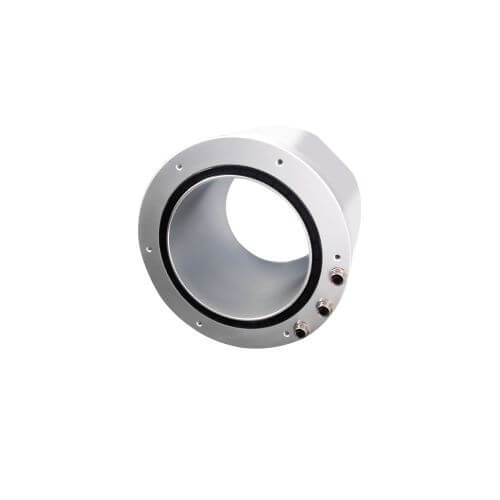

Pancake Slip Rings
These slip rings, known for their distinctively flat ‘pancake’ design, are ideal for applications where the length is restricted but there’s a certain freedom in diameter. To put it simply, these slip rings are all about fitting into tight vertical spaces.
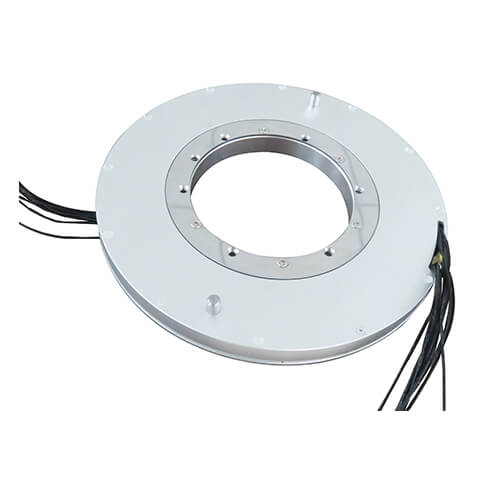

Mercury-Filled Slip Rings
Moving onto specialized slip rings, the mercury-filled slip rings utilize liquid metal. The liquid metal, in this case, mercury, provides low resistance and allows for high-speed data and signal transmission. In addition to this, these slip rings provide long life and maintenance-free operation. They are used in situations where minimal resistance and high speed are aesthetic aspects, but the use of mercury does entail careful handling.
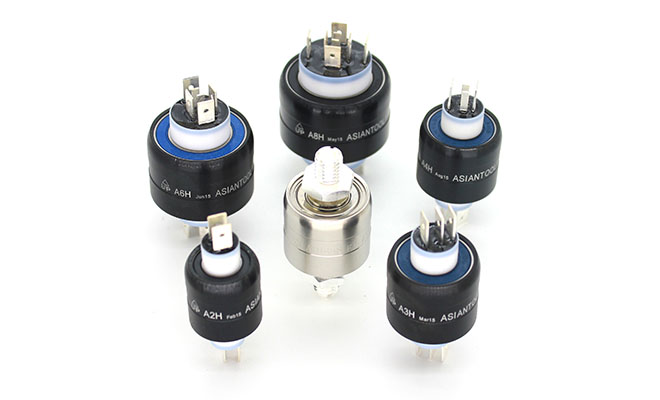

Modular Slip Rings
Last but not least, we have modular slip rings – the ‘Swiss army knife’ of slip rings. These come with high configurability that allows them to be tailored to a wide variety of situations. These slip rings can be easily modified to accommodate power, signal, and even data transmission to suit different combinations of applications, offering unprecedented flexibility.

In summary, each of these slip ring collectors has its strengths and is well-suited to particular applications. The choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the system, be it space, speed, adaptability, or a combination of these factors, ensuring an ideal fit for every unique requirement.
Electrical Slip Ring Collector
An electrical slip ring collector, often referred to simply as a slip ring, is an electromechanical device designed to transmit electrical power and signals from a stationary structure to a rotating one. It enables continuous electrical connection between rotating and stationary parts without restricting the motion of the rotating part, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted data or power transfer.
Key Components of a Slip Ring Collector
- Stationary Part (Stator)
- This part remains fixed and usually connects to the power source or control system.
- It provides an electrical connection to the internal rings or circuits.
- Rotating Part (Rotor)
- This part rotates with the equipment or machinery.
- Wires connected to the rotor receive the transmitted power or signals from the stationary part.
- Slip Rings
- Conductive rings are made from copper, brass, or other conductive materials.
- These rings are mounted on the rotating shaft and carry electrical signals or power continuously.
- Brushes
- Made from graphite, carbon, or precious metals, brushes remain in contact with the slip rings.
- They act as the medium for the transfer of electricity between stationary and rotating components.
- Housing and Bearings
- The slip ring assembly is enclosed in a protective housing to prevent contamination and wear.
- Bearings are included to ensure smooth rotation and reduce mechanical friction.
Electrical slip ring collectors play a vital role in many industries by enabling seamless transmission of power and data between stationary and rotating components. Their versatility in handling both power and signals makes them indispensable in applications such as wind turbines, electric motors, medical devices, and automation systems. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the brush-ring contact are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
How It Works: Slip Ring Collector
A slip ring collector is a mechanical device that facilitates the transfer of power, signals, or data from a stationary component (stator) to a rotating one (rotor) without interrupting electrical continuity. Below is a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
Step-by-Step Working Principle
1. Basic Setup
- The slip ring assembly consists of one or more metallic rings mounted on a rotating shaft.
- Brushes, typically made from carbon, graphite, or other conductive materials, are placed against the rings.
- The stationary part (the brushes) is connected to an external power source or signal input, while the rotating part (the rings) connects to equipment that rotates continuously, such as motors, turbines, or antennas.
2. Power or Signal Transfer through Rings and Brushes
- Brushes rest on the rotating slip rings, making continuous electrical contact despite rotation.
- When the shaft rotates, the rings rotate along with it, but the brushes remain fixed in place.
- Current or signals from the stationary part flow through the brushes and into the slip rings, which then transfer them to the rotating part.
- The circular shape of the rings allows the brushes to maintain uninterrupted contact even as the shaft spins.
3. 360-Degree Continuous Rotation
- Because the rings rotate along with the shaft, the equipment can spin infinitely without twisting or tangling wires.
- This is particularly useful for devices like wind turbines, cranes, or rotating radars, where continuous rotation is essential.
4. Handling Different Types of Transmission
- Power Transmission: The slip rings carry electrical current to power rotating equipment, such as in generators or motors.
- Signal Transmission: In applications like robotics or data transmission systems, the slip ring can transfer analog or digital signals.
- Hybrid Systems: Some slip rings handle both power and signals simultaneously by using multiple isolated rings within the same unit.
- High-Frequency or Optical Transmission: Advanced slip rings, like fiber-optic ones, transfer data without electrical interference, using light signals.
5. Brush-Ring Interface: Ensuring Smooth Transfer
- The friction contact between brushes and rings ensures a continuous path for electricity.
- Brush pressure is optimized to maintain contact while minimizing wear.
- Self-lubricating materials or brush maintenance systems are often used to ensure reliable long-term operation.
6. Minimizing Electrical Noise and Resistance
- In high-precision applications, low-resistance contact between the brushes and rings is essential to prevent signal distortion or voltage drops.
- To further reduce interference, gold-plated rings or composite brushes are used in certain high-frequency systems.
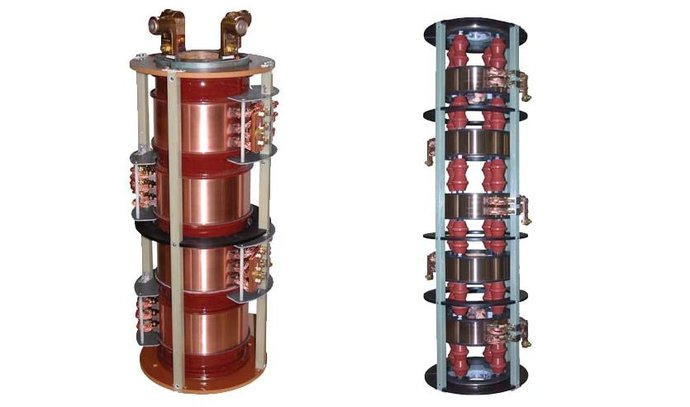

Visualizing the Process
- Stationary Input: The brushes connect to the electrical source or control unit.
- Rotating Transmission: As the slip rings spin with the rotating shaft, they carry the electrical signals or power continuously.
- Rotating Output: Wires connected to the rings distribute the transmitted power or signals to the rotating equipment.
Key Benefits of Slip Ring Collectors
- Unrestricted Rotation: Continuous 360-degree motion without cable twisting.
- Versatile Transmission: Capable of handling both power and signal/data transmission.
- Compact Design: Saves space by eliminating the need for bulky cables in rotating machinery.
- Reliable in Motion: Reduces wear on cables and ensures uninterrupted operation.
This mechanism ensures seamless electrical connection between stationary and moving systems, making the slip ring collector essential for machines that require continuous rotation and consistent power or signal transfer.
Slip Ring Collector Assemblies Assembly
A slip ring collector assembly is a system that ensures smooth electrical transmission between stationary and rotating components. Below is a detailed explanation of its key components and how it is assembled.
Components of a Slip Ring Collector Assembly
- Conductive Rings (Slip Rings)
- Made from materials such as copper, brass, or silver-plated alloys for high conductivity.
- Mounted on a rotating shaft to transmit power or signals continuously.
- Brushes
- Typically composed of graphite, carbon, or metal composites to ensure reliable contact.
- Pressed against the rotating rings to transfer electrical energy or signals.
- Mounted in spring-loaded holders to maintain consistent pressure.
- Brush Holders
- Mechanical structures that house the brushes and ensure alignment with the rotating rings.
- Insulating Materials
- Non-conductive spacers or coatings are placed between adjacent rings to prevent short circuits.
- Commonly made from ceramics or high-strength polymers.
- Housing/Enclosure
- A protective shell to shield the assembly from dust, moisture, and contaminants.
- Made from aluminum, stainless steel, or durable plastics based on application needs.
- Bearings
- Precision ball or roller bearings are used to ensure smooth, low-friction rotation.
- Shaft or Rotor
- The rotating part that holds the slip rings and connects to the rotating machinery.
- Stationary Wiring Terminals
- Provide connection points to integrate the slip ring assembly with external electrical systems.
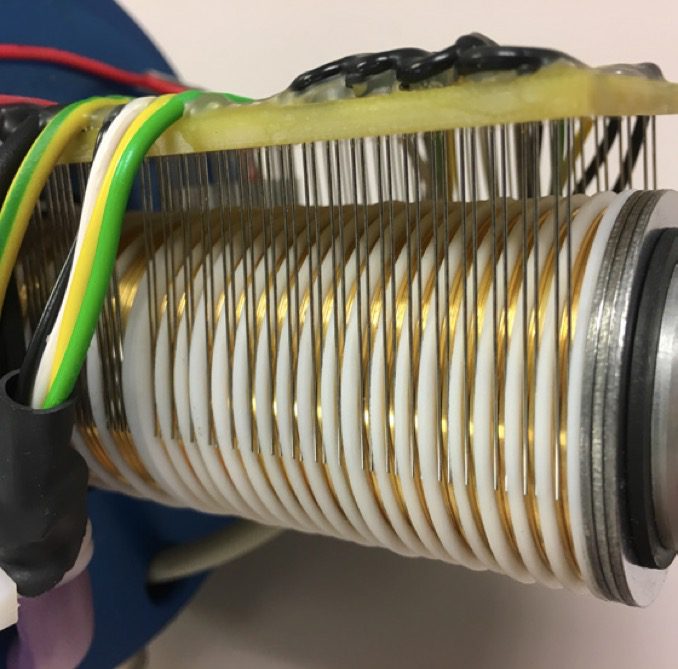
Assembly Process
- Preparing the Shaft and Slip Rings
- Slip rings are mounted on the rotating shaft with proper spacing using insulating materials.
- The rings are locked in place with spacers to maintain alignment and prevent electrical shorts.
- Installing Bearings
- Bearings are fitted onto the shaft or inside the housing to allow smooth rotation.
- Lubrication is applied to the bearings to minimize friction and wear.
- Attaching Brushes and Holders
- Brushes are inserted into their holders and aligned with the slip rings.
- Springs in the holders apply constant pressure on the brushes to ensure consistent contact.
- Electrical Connections
- Wires are connected to the brushes to link the assembly to the power or signal source.
- The rotating side of the rings connects to wires that transmit power or data to the rotating equipment.
- Installing Insulation Layers
- Insulating layers are placed between rings to ensure the electrical isolation of different circuits.
- This is especially important in hybrid systems transmitting multiple signals or power lines.
- Assembling the Housing
- The shaft, slip rings, brushes, and holders are placed inside the protective housing.
- The housing is sealed with gaskets or O-rings to prevent contaminants from entering.
- Final Alignment and Testing
- The assembly is checked for smooth rotation and proper alignment.
- Electrical continuity and signal transmission are tested to ensure performance under operational conditions.
Quality Checks and Maintenance
- Inspecting Brush Wear: Brushes need regular checks for wear and proper contact.
- Electrical Noise Testing: Ensures minimal interference during signal transmission.
- Lubricating Bearings: Periodic lubrication is required to prevent friction and overheating.
- Sealing Integrity: The housing should be inspected to ensure it remains dust- and moisture-proof.
A well-assembled slip ring collector ensures efficient, continuous operation by allowing smooth electrical transmission between stationary and rotating components. Proper installation, maintenance, and alignment are critical for long-lasting performance.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Slip Ring Collector
Slip ring collectors might seem like simple devices, but choosing the right one for a specific application can be a complex decision involving several considerations. The interplay of various factors can affect the performance, durability, and overall effectiveness of the slip ring for your system.
Electrical Requirements
One does not fit all when it comes to slip rings’ power handling and signal transmitting abilities.
- Current Capacity: This parameter defines the amount of electrical current a slip ring can carry. This depends on your system’s power requirement and needs to be carefully assessed to ensure efficient operation.
- Voltage Capacity: It refers to the maximum voltage a slip ring can withstand without arcs or breakdowns. The right slip ring should fulfill your equipment’s voltage requirements without compromising safety or functionality.
- Circuits: The number of circuits or channels needed for the transmission of signals and power is another crucial consideration. Ensure your chosen slip ring has a sufficient number of circuits to accommodate your system’s electrical pathways.
Mechanical Requirements
The physical aspects like size, speed, and mounting play a vital role in the suitable deployment of slip rings.
- Rotational Speed: This involves the maximum rotations per minute (RPM) the slip ring can handle without mechanical failures. High-speed applications will need slip rings designed to withstand such rapid movement.
- Mounting Options: Depending on your system’s design, different mounting options, including flange, bore, or end-of-shaft, might be necessary. Therefore, the slip ring you choose must infer compliance with your mounting needs.
- Size Restrictions: Depending on the spatial availability, you might need a compact slip ring like the capsule, or if height is a constraint, a pancake slip ring may be more suitable.
Environmental Conditions
Slip rings operational sturdiness directly correlates with the environmental factors it’s subjected to.
- Temperature Range: Based on the application environment, the slip ring should be resistant to the maximum and minimum temperature extremes without its performance being impacted.
- Dust and Moisture Protection: The dust and moisture protection capacities, denoted by IP ratings, are critical, especially for outdoor or industrial applications. These factors could affect the flow of transmission, hence choosing a slip ring with suitable resistance is crucial.
- Corrosion Resistance: Particularly important in marine or chemically-intensive environments, the slip ring materials must resist corrosion to prevent premature failure.
Lifespan and Maintenance
The durability of the slip ring and its maintenance requirements affect its overall operational costs. Choosing a robust slip ring that requires minimal maintenance can reduce sudden system downtime and long-term costs.
Cost and Budget
While all the above factors are essential considerations, it’s important not to overlook the cost constraints. The chosen slip ring should not only meet the system requirements but also align with your budget.
In conclusion, selecting an appropriate slip ring collector is a process that requires careful consideration of various electrical and mechanical requirements, as well as environmental conditions, lifespan, maintenance, and cost. Each of these factors contributes to its performance and effectiveness in the intended application. By taking these into account, we can ensure a slip ring’s optimal compatibility and durability and prevent unnecessary costs and maintenance problems in the long run.
Customized Solutions and Benefits
Often, the standard off-the-shelf options may fall short of meeting the specific requirements of a particular electromechanical system. In such situations, a customized slip ring collector can be the ideal solution. Customized slip rings are tailored to the exact specifications of any given application, ensuring a highly efficient and seamless operation. They embody the concept of the perfect ‘fit-for-purpose’ solution. The following discusses when and why customized slip rings might be necessary and the benefits of opting for them.
Situations That Call for Customized Slip Ring Collectors
- Unique System Requirements: Certain applications might have unique or complex system requirements that do not fall under the typical specifications provided by standard slip rings. This could range from something as complex as a unique combination of power and signal transfer to specific mechanical constraints like an unusual size or mounting style.
- Extreme Environments: Sometimes, electromechanical systems need to function in extreme environments. This could be at exceptionally high or low temperatures, submerged in water or exposed to harsh chemicals, or subjected to extreme vibrations or dust exposure. Standard slip rings might not always provide the necessary durability and robustness required for these environments.
- High-Performance Applications: In high-performance applications such as aerospace or cutting-edge medical equipment, any deficiencies in the slip ring’s performance can significantly impact the outcome. These scenarios often demand bespoke components, including custom-designed slip rings, to ensure maximum reliability and precision.
Benefits and Implications of Customized Designs
Opting for a customized slip ring collector presents several advantages:
- Optimized Performance: Custom slip rings are designed based on the precise requirements of the system, ensuring an optimized performance. They can enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of the system more effectively than standard slip rings.
- Reduced Maintenance and Downtime: Although customized solutions might cost more upfront, they often lead to lower maintenance costs and system downtime in the long run, as they are specifically designed and built for the intended application.
- Space Maximization: Custom designs can be made in specific shapes and sizes, fully maximizing the available space in your system. They can fit seamlessly into the design without necessitating changes or adjustments to other components.
- Longevity: Custom-built slip rings are typically robust and designed to meet or exceed the application’s requirements, leading to a longer lifespan and better return on investment.
In essence, while standard slip ring collectors are suitable for many applications, unique or challenging scenarios may call for customization. The ideal slip ring collector design may result from a financial investment in customization, but it’s a worthwhile pursuit for reducing system downtimes, enhancing performance, improving durability, and overall, saving resources over the long term.
Application Examples of Slip Ring Collectors
Slip ring collectors are ubiquitous across a broad spectrum of industries. Their ability to facilitate the transmission of power and signals between stationary and rotating parts is incredibly valuable in various fields. Below, we explore some typical applications where slip-ring collectors demonstrate their worth.
- Wind Turbines: Wind turbines generate electricity by leveraging the force of wind to rotate large blades. These blades are connected to a rotor which is essentially a rotary system. The conversion system changes mechanical energy to electrical energy (generator) and the control systems are stationary. Power and data signals need to be transferred between the stationary and rotating components, and that’s where slip ring collectors come into play, enabling constant rotation without compromising power or data transmission.
- Robotics and Automation: Robotic arms, automation equipment, and AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) often feature rotating joints or parts. These joints need to transfer control signals to and from the system’s stationary part. By using slip ring collectors, robotics achieve smooth, uninterrupted operation, which is vital for maintaining productivity and precision.
- Medical Equipment (e.g., CT Scanners): Medical imaging devices such as CT scanners rely heavily on slip-ring technology. The patient remains stationary while the scanner rotates around them to capture detailed cross-sectional images of the body. A slip ring collector enables these images’ transmission whilst powering the rotating gantry, ensuring seamless operation for more accurate diagnoses.
- Surveillance Systems (e.g., radar platforms): Radar platforms, CCTV cameras, and other surveillance equipment often require 360-degree rotation to provide comprehensive coverage. Slip ring collectors enable these devices to rotate continuously while transmitting data and power to the surveillance systems, significantly aiding security and monitoring systems.
- Rotating Stages and Lighting Systems: In entertainment systems and stage setups, lights and speakers often need to rotate or pan to provide a surround sound or light effect. Slip ring collectors enable this movement while maintaining audio-visual signals and power transmission, resulting in dynamic and impressive performances without interruptions.

In essence, any application requiring power or data to be transmitted between stationary and rotating components can benefit significantly from slip ring collector technology. These application examples are just the tip of the iceberg, demonstrating the slip ring collectors’ versatility in fulfilling a vast range of industrial operations, from renewable energy generation to healthcare and entertainment technology.
Slip Ring Collectors Installation and Integration Tips
The effectiveness of a slip ring collector greatly depends on its correct installation and integration within an existing system. Each component’s successful implementation, including slip rings, impinges on the overall system’s efficacy. Furthermore, properly maintained electrical connections and alignment are vital to prevent unnecessary issues and downtime. Herein, we explore some key tips on slip ring collector installation, integration, and maintenance.
Installing and Integrating a Slip Ring Collector
- Understand the Requirements: Before undertaking installation, it’s crucial to fully understand the system’s electrical and mechanical requirements. This requires knowledge of the system’s power and signal specifications, rotational speed, mounting options, and spatial availability.
- Check the System Compatibility: Before commencing the installation, verify that the chosen slip ring collector is compatible with the system’s requirements and environment. This includes checking the electrical specifications and the physical dimensions of the slip ring collector.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: The installation process should strictly adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions. Deviating might lead to improper installation, resulting in issues such as subpar performance or even damage to the slip ring collector or system itself.
- Professional Installation: If possible, have a qualified professional oversee or perform the installation, especially for complex or high-performance systems. The nuances of proper installation might require expertise and experience to be correctly implemented.
Maintaining Proper Electrical Connections and Alignment
- Regular Inspection: Regularly inspect the slip ring collector for any signs of wear or damage. Over time, electrical connections might loosen or wear down, which could lead to inefficiencies or failures.
- Proper Wiring and Connection: Ensure that all wiring and connections correlate with the system’s electrical requirements. Any mismatches could lead to insufficient power transmission, signal interference, or potential damage.
- Keep Clean and Dry: As much as possible, keep the slip ring collector clean and dry. Dust, moisture, or debris might interfere with the electrical connections and transmission, compromising the performance.
- Timely Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance based on the manufacturer’s recommendations. This typically involves cleaning and inspection, along with any necessary part replacements.
In conclusion, the proper installation and integration of a slip ring collector are integral to its effective functioning within a system. Carefully maintain electrical connections and alignment, and conduct regular inspections to identify and address any issues as they arise. This proactive approach will go a long way in preserving the longevity of the slip ring and the entire system, reducing the chance of untimely disruptions.
Best Practices for Prolonging Slip Ring Collector Lifespan
To maintain an efficient and reliable electromechanical system, it is vital to optimize the lifespan of each of its components, including the slip ring collector. Adherence to recommended maintenance routines and the adoption of best practices can significantly extend the operational lifespan of these essential components. Below, we provide more details on these vivifying guidelines.
Maintenance Recommendations
- Cleaning: Depending on the environment where the slip ring operates, it may accumulate dust or debris over time. Regular cleaning, in adherence to manufacturer recommendations, is important to prevent this accumulation from impeding electrical contact and causing wear on the contact surfaces.
- Inspection: A thorough inspection of the slip ring collector should be conducted regularly, also in line with manufacturer recommendations. Inspections can help detect any changes or anomalies early, including loose parts, partial wear, or damaged enclosures before they escalate into serious problems.
- Replacement of Worn Parts: Over time, parts of the slip ring may wear out due to constant rotation and contact. Regular inspection will reveal when these parts are near the end of their useful life, allowing you to replace them proactively and prevent malfunctions or failures.
Minimizing Wear and Tear
- Ensuring Proper Lubrication: If your slip ring collector requires lubrication, ensure it is adequately lubricated to minimize friction between the rotating surfaces. Always use the lubricant recommended or approved by the slip ring manufacturer.
- Alignment and Balanced Rotation: Ensure the slip ring is correctly aligned and functioning in a balanced rotation. Misalignment or imbalance might speed up wear, lower efficiency, and shorten the lifespan of the slip ring. Regular inspection will help detect and rectify these issues quickly.
Overall, prolonging the lifespan of a slip ring collector is a direct result of diligent maintenance and adherence to best practices. Regular cleaning and inspections, in line with the manufacturer’s guidelines, are essential and should be complemented by proactive care and maintenance. Furthermore, minimizing wear and tear through proper lubrication and alignment can significantly improve the slip ring’s overall efficiency and lifespan, ensuring a longer and healthier life for the entire electromechanical system.
Slip Ring Collector: Service Life
The service life of a slip ring collector refers to the length of time it can operate reliably before requiring maintenance or replacement. Various factors impact its longevity, such as material quality, environmental conditions, load characteristics, and the level of maintenance.
Key Factors Affecting Service Life
- Brush and Ring Wear
Friction between the brushes and slip rings causes gradual wear. The type of brush material plays a crucial role:- Graphite brushes have a longer lifespan but generate conductive dust.
- Metal brushes offer better conductivity but cause quicker wear on the rings.
- Spring tension needs to be optimal; too much tension causes excessive friction, while too little may result in arcing.
- Operating Environment
- Temperature extremes can degrade the brush material, insulation, or lubrication.
- Humidity and moisture may cause corrosion on rings, lowering performance.
- Dust and contaminants affect the brush-ring interface, leading to increased friction and electrical noise.
- Electrical Load
- High current or voltage loads can cause heating, increasing wear over time.
- Unstable electrical loads can lead to arcing and faster degradation of brushes and rings.
- Rotation Speed
- High-speed rotation leads to faster friction-induced wear.
- Slow speeds may result in poor brush contact and increased arcing, impacting signal quality.
- Maintenance Practices
- Regular cleaning of brushes and rings prevents dust accumulation.
- Timely brush replacement ensures optimal performance and prevents ring damage.
- Proper bearing lubrication reduces mechanical friction and extends the life of the entire assembly.
Typical Service Life Estimates
- Brushes:
Brushes typically last between 10,000 to 50,000 hours, depending on material quality and the operating conditions. - Slip Rings:
Slip rings can last 50,000 to 100,000 hours with proper care, though excessive wear can shorten this lifespan. - Bearings:
Bearings, if correctly maintained and lubricated, generally last between 50,000 to 100,000 hours.
Tips to Extend Service Life
- Select Appropriate Brushes
Choose brushes suited to the application. Graphite brushes are better for signals, while metal brushes are more suitable for high-current applications. - Inspect Regularly
Perform periodic inspections to detect wear and replace brushes before they degrade ring surfaces. - Ensure Proper Sealing
Protect the assembly from dust and moisture to prevent contamination. - Control Electrical Loads
Avoid exceeding the rated current and voltage, which could cause overheating. - Lubricate Bearings Properly
Routine lubrication of bearings minimizes mechanical wear and ensures smooth operation. - Monitor Temperature and Cooling
Install cooling systems if necessary to prevent overheating in high-temperature environments.
A slip ring collector can achieve a service life of 10 to 20 years with proper maintenance and optimal operating conditions. Regular inspections, brush replacements, and environmental protection are essential to maximize performance. Careful monitoring of electrical loads and lubrication of bearings will ensure that the system remains reliable over the long term.
Latest Trends and Developments in Slip Ring Collectors
As with any technology, the field of slip ring collectors continually advances and reinvents itself in response to emerging opportunities and challenges. To stay abreast of the latest developments in the industry, it is crucial to understand the most recent trends and identify potential advancements that could influence future slip ring collector designs. This awareness can facilitate strategic investments, advantageous collaborations, and innovative product or service offerings.
Overview of Current Industry Advancements and Innovations
- Miniaturization: With numerous applications demanding smaller and more portable devices, the trend of miniaturization has swept across various industries, and slip ring collectors are no exception. Manufacturers are now developing compact, lightweight slip ring designs that can cater to the specific needs of small-scale equipment without compromising performance.
- Higher Data Rates: There is an ever-increasing demand for faster data transfer in various sectors, including telecommunications, aerospace, and defense systems. In response, slip ring manufacturers are leveraging advancements in electrical contact materials and realizing designs that can handle higher data rates, while minimizing signal loss and interference.
- Integration of Sensors and Electronics: Combining slip rings with various sensors and electronics allows for more advanced control and monitoring capabilities. This integration results in greater automation and more efficient systems in applications such as robotics, wind turbines, and heavy machinery.
Impact of New Materials and Technologies on Future Slip Ring Collector Designs
- New Contact Materials: The emergence of new materials can enable the development of slip ring collectors with superior electrical and mechanical characteristics. These materials may have lower electrical resistance, improved wear resistance, or excellent lubrication properties, resulting in longer-lasting, more efficient slip rings.
- Wireless Transmission: As wireless communication technology improves, contactless slip rings are gaining more appeal in certain applications. By adopting inductive or capacitive coupling to transfer power and signals, contactless slip rings can eliminate wear, thereby improving durability and reducing maintenance requirements.
- Modular Designs: The use of modular slip ring collectors has grown recently, with their designs offering a level of flexibility and adaptability for various applications. These modular designs permit customization, ease of maintenance, and the potential for cost-efficient upgrades.
Being able to respond to these latest trends and developments in slip ring collectors can position a company to thrive in an evolving global landscape. Keeping ahead of the curve in industry advancements, new materials and technologies present incredible growth opportunities. This adaptability and innovative foresight enable stakeholders to invest wisely, make informed decisions, and break new ground in the constantly evolving slip ring collector market.
Conclusion
Overall, selecting the perfect slip ring collector is of paramount importance for your system’s effective and efficient operation. A thorough understanding of critical factors and maintaining best practices will ensure your slip ring performs optimally for a longer period, thus enhancing your system’s overall productivity. Be sure to monitor the latest industry trends and innovations, as they may offer key insights to continually evolve your operational efficiency.
Have unique slip ring requirements? Tell us through this form.


