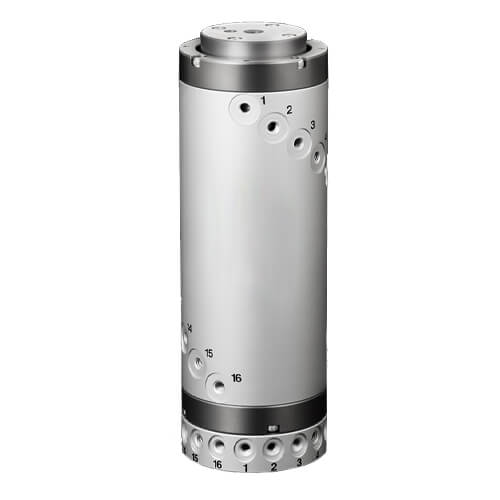
An SMA Rotary Joint, in its simplest definition, is a device that combines SubMiniature version A (SMA) connectors with a rotary joint designed for radio frequency (RF) applications. These joints significantly stand out due to their ability to rotate while maintaining continuous electrical connection, hence facilitating efficient signal transmission. Under this, SMA Rotary Joints enable RF signals to be transmitted between fixed and rotating parts effectively, playing an instrumental role in ensuring the seamless integration of RF systems.
In the modern era, the relevance of the SMA Rotary Joint cannot be understated. The recent surge in technological and communication advancements, especially those relying on RF systems, has created an increased demand for devices that can ensure reliable and consistent signal transmission. Whether in satellite communication, military radar systems, mobile communication equipment, or test and measurement instruments, the SMA Rotary Joint finds itself central to various applications. Its ability to function efficiently, even under high-frequency rotation, makes it a key facilitator of these advanced systems. As such, SMA Rotary Joints contribute considerably to advancements and innovations seen across numerous sectors in today’s interconnected world.
Basics of SMA Rotary Joint
Discuss the SMA Connector in the Context of Radio Frequency Applications.
SubMiniature version A (SMA) connectors are a type of RF connector developed during the 1960s to offer flexibility and dependable performance for coaxial cables with RF signals. These connectors have proven themselves essential due to their ability to ensure efficient and accurate signal transmission at high frequencies, up to 18 GHz. Used widely for communicative and technical applications, they are inherently designed to minimize reflections and loss, thereby providing reliable and stable connections, and cruxes for high-quality radio frequency applications.

Explain how a Rotary Joint Functions.
A rotary joint, as its name suggests, is an electromechanical device that allows rotation of the part of a machine while transmitting power, electric signals, or data from a stationary part to a rotating one or vice versa. It equips the equipment with the capacity to maintain continuous electrical connection even when one part of the joint is rotating, significantly boosting signal transmission capabilities. Furthermore, they are adept at managing multiple signals simultaneously and can accommodate a wide array of frequencies, making them an excellent choice for complex and power-packed applications.
Combine these Two Concepts to Fully Describe the SMA Rotary Joint.
Bringing together these two integral components—the SMA connector and rotary joint—leads to the creation of the SMA Rotary Joint. This ingenious combination equips the joint with an unmatched ability to ensure seamless radio frequency signal transmission between fixed and rotating parts. The SMA connector brings its high-frequency handling capabilities, delivering power and reliability to the mix. On the other hand, the rotary joint offers the dynamism of maintaining electrical connection regardless of rotation, lending versatility and flexibility. Together, they form the SMA Rotary Joint, an indispensable entity in various modern-day applications.

Key Components of SMA Rotary Joint
Description of Each Integral Part and its Function
An SMA Rotary Joint consists of several integral components, each playing a pivotal role in the overall operation of the device:
- Outer Conductor: This serves as the grounding for the RF circuit. Since the signals’ efficiency strongly relies on a stable grounding channel, the outer conductor’s design is fundamental to ensuring the transmission line’s impedance remains consistent and losses are minimized.
- Inner Conductor: This is the part through which the actual signal transmission happens. The inner conductor carries the electrical signal across the joint, hence its construction material and design determine the signal transmission’s effectiveness.
- Insulator: Positioned between the outer and inner conductors, the insulator’s function is to provide a physical separation while enabling electrical isolation between the two conductors. The choice of insulator material is critical, as it needs to withstand the mechanical stresses of rotation while offering excellent electrical insulation to maintain signal integrity.
How These Parts Collaborate to Make the Joint Work
The collaboration between these components is what makes the SMA Rotary Joint a powerhouse in RF signal transmission. The electrical signal initiated from the inner conductor moves through the joint, with the insulator maintaining the signal’s integrity by preventing any potential interference from the outer conductor. The outer conductor, in tandem, provides the necessary grounding to maintain the transmission line’s characteristic impedance.
What makes an SMA Rotary Joint outstanding is how these elements work in unison, delivering flawless performance even when in rotation.
This ability to maintain electrical connection during rotation without signal degradation is the fruit of these parts’ intricate collaboration, illustrating the beauty of the SMA Rotary Joint’s design and functionality.
Working Principle of SMA Rotary Joint
Full Technology Breakdown of the Rotary Joint
The working principle of a rotary joint is to provide continuous electrical connection while allowing rotational motion. It consists of a stationary and rotating section, with internal contact surfaces engineered to sustain rotation while retaining signal integrity.
The stationary section is connected to a fixed part of the machine or application, often through an SMA connector, and the rotating section is connected to the rotating part. As these two sections interconnect, typically through an electrically conducting component such as a brush or a specialized interface design, they preserve the electrical connection even during rotation.
To achieve this, however, rotary joints require careful engineering to ensure minimal wear and noise, low contact resistance, and high signal quality over extended periods of rotation and varying loads. Moreover, depending on the application and frequency range, rotary joints may adopt different designs to handle single or multiple signal channels, accommodating unique requirements.
Discuss How the SMA Connector Supports This Function
The SMA connector’s role is crucial in supporting and augmenting the rotary joint’s function. Capable of performing well at higher frequencies (up to 18 GHz) with dependable connection and minimal signal loss, SMA connectors play a critical part in ensuring radio frequency applications’ seamless operation.
Fill Out the Form for a Personalized SMA Rotary Joint Quote.
SMA connectors feature a threaded coupling mechanism that allows them to be securely fastened to the rotary joint, creating a reliable bond and eliminating the risk of disconnection during rotation. Their compatibility with a variety of transmission lines, such as coaxial cables, provides additional flexibility to the SMA Rotary Joint, making it suitable for various applications.
In essence, the combination of an SMA connector and the rotary joint results in the SMA Rotary Joint, a powerful and versatile device that facilitates efficient and reliable RF signal transmission between stationary and rotating sections while maintaining the continuous electrical connection vital for modern communication and radar systems.
Types of SMA Rotary Joints
Discuss the Variants of SMA Rotary Joint Available in the Market
Given the diverse range of applications, SMA Rotary Joints are available in a variety of configurations. Broadly, they can be classified based on the number of channels they accommodate:
- Single Channel Rotary Joints: Single channel rotary joints are simplest in design and primarily allow for one RF signal to be transmitted between a stationary and rotating part of a setup. These are commonly used in simpler, cost-sensitive applications with limited signal requirements.
- Multi-Channel Rotary Joints: For more complex systems requiring the transmission of multiple RF signals simultaneously, multi-channel rotary joints come into play. Such joints have several isolated channels, thus enabling them to handle multiple distinct signals without interference.
Pros and Cons of Each Type
- Single Channel Rotary Joints
- Pros: They are relatively less complex and more affordable, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious projects and applications with limited signal requirements.
- Cons: Their applicability is limited by their single-channel capacity. They are not ideal for complex RF systems requiring the transmission of multiple signals simultaneously.
- Multi-Channel Rotary Joints
- Pros: The ability to handle multiple separate signals makes them versatile and ideal for complex RF systems, such as telecommunications and radar systems.
- Cons: They tend to be more complex and expensive due to the need for careful isolation of each channel, which can escalate the overall costs and technical requirements during installation and maintenance.
In conclusion, the selection between a single-channel or multi-channel SMA Rotary Joint depends largely on the specific requirements of the application, with each offering its unique set of advantages and potential limitations.
Applications of SMA Rotary Joint
Explain Where and Why SMA Rotary Joints Are Typically Used.
Given their ability to maintain constant electrical communication between stationary and rotating sections, SMA Rotary Joints find a vast array of applications across industries. They are popularly utilized in systems where RF signals need to be transmitted without disruption despite rotary movement. This includes radar systems, satellite communication antennas, measurement systems, and a plethora of high-frequency rotary applications. Their capacity for high-frequency signal transmission, robust build, and durability against repeated rotational operations make them a top choice in these settings.

Examples and Case Studies from Different Industries
- Satellite Communications: In the field of satellite communications, SMA Rotary Joints enable the constant transmission of signals between the ground station (stationary) and the satellite dish (rotating) as it tracks the satellite’s movement. With the use of a multi-channel SMA Rotary Joint, different frequency bands can be transmitted simultaneously, fulfilling the communication and tracking roles of the system.
- Radar Systems: Radar systems equipped with rotating antennas utilize SMA Rotary Joints to maintain seamless connections for the transmission of RF signals. The joints ensure that the radar can accurately track and identify objects, as the signals are transmitted without disruption even when the antenna rotates.
- Medical Equipment: In medical devices such as CT scanners, SMA Rotary Joints facilitate seamless transmission of RF signals between the stationary and the rotating part of the machine. On one hand, the joint aids in transmitting control and power signals to the rotating gantry that houses the X-ray tube and detectors. On the other hand, it helps transfer the acquired data from the rotating part back to the stationary system for image reconstruction.
These examples illustrate the crucial role SMA Rotary Joints play in diverse applications across numerous industries, validating their reputation as a quintessential element in any system requiring high-frequency rotary operations.
Installation and Maintenance of SMA Rotary Joints
A Step-By-Step Guide to Installing an SMA Rotary Joint
Here are the general steps in installing an SMA Rotary Joint:
- Step 1: Before the installation, inspect the SMA Rotary Joint for potential damages incurred during transportation.
- Step 2: Identify the rotating and stationary sections of the joint.
- Step 3: Connect the rotating part of the joint to the rotating machine part, ensuring the connection is secure.
- Step 4: Connect the stationary part of the joint to the stationary section of your system.
- Step 5: Be cautious while threading connectors and do not over-tighten as it may impact the performance of the device or even damage it.
- Step 6: Once both sections are securely connected, perform a dry-rundry to ensure everything is working correctly.
Tips for Maintaining and Extending the Life of Devices
Regular maintenance is crucial to extend the service life of SMA Rotary Joints. Here are some maintenance tips:
- Follow recommended maintenance schedules and procedures provided by the manufacturer.
- Regularly perform a visual inspection for damages and wear and tear, especially in the connectors.
- Ensure the device is not exposed to harsh environmental factors including extreme temperature, dust, excessive moisture, or corrosion-causing elements.
- Implement regular system performance checks to monitor the rotary joint’s performance and potential decline in signal quality.
What to Do When Troubleshooting is Necessary
If the SMA Rotary Joint fails to operate as expected, the following steps could help in troubleshooting:
- Inspect the Joint: Check for visible signs of damage or wear. Look specifically at the SMA connectors, if there is any sign of damage or corrosion, they may need to be replaced.
- Check the Connections: Ensure the joint is correctly and securely connected to the machinery. A loose connection can result in interrupted signal transmission.
- Test the Performance: Use appropriate testing equipment (like a network analyzer) to check the transmission characteristics and overall performance of the rotary joint.
- Contact the Manufacturer: If all else fails, contact the manufacturer or your service provider. They can provide specific guidance and potentially service the component for you.
Remember, while these steps can guide you in a general sense, always refer to the device’s specific manual or manufacturer guidelines for precise instructions and maintenance schedules.
Buying Guide for SMA Rotary Joint
Factors to Consider When Purchasing an SMA Rotary Joint
When aiming to buy SMA Rotary Joints, consider the following factors:
- Application Needs: The type of application will guide your decision. If you require transmission of a single RF signal, a single-channel rotary joint will suffice. However, complex systems requiring the transmission of multiple RF signals simultaneously will need a multi-channel rotary joint.
- Feasibility: Consider the size, weight, and design of the product as per the feasibility of your setup.
- Frequency Range: SMA connectors typically operate up to 18GHz, ensure this frequency range aligns with your system’s requirements.
- Durability & Lifespan: Check the durability and lifespan offered by the manufacturer of the product. This will give an idea about the product’s quality and its ability to withstand rigorous conditions.
- Manufacturer’s Reputation: Companies with a good reputation tend to offer good quality products and better after-sales service.
A Comparison of Multiple Brands
Some prominent manufacturers in the SMA Rotary Joints market include:
| No. | Manufacturer | Website |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hangzhou Grand Technology | https://www.grandslipring.com/ |
| 2 | Moog Inc. | https://www.moog.com/ |
| 3 | Stemmann-Technik | https://www.stemmann.com/en/home |
| 4 | Schleifring | https://www.schleifring.com/ |
Hangzhou Grand Technology
Hangzhou Grand Technology Co., Ltd. started as a special slip ring manufacturer in 2011. Grown into slip rings, rotary joints, and slip ring assembly experts of today with 6,000 square meter manufacture complex.
Obtained ISO9001, Rosh, CE, and GJB9001B certificates a number of slip rings, rotary joint patents, and proud of our products can meet military grade. Collaborated with universities, institutes, and renowned factories across Asia and Europe including Panasonic, SIEMENS, CSIC, SAMSUNG, HUAWEI, etc.
Moog Inc.
Moog is a leading supplier of high-performance slip rings for various industries, including aerospace. Among their offerings, Moog’s SR Series Slip Rings are designed for the demanding environments of helicopters, excelling in performance, reliability, and customization potential.
Stemmann-Technik
Stemmann-Technik, a part of the Conductix-Wampfler Group, offers a broad range of slip rings, including solutions for helicopters. Their Livietta Slip Ring Assemblies are designed explicitly for harsh and demanding environments in the aviation sector, providing reliable signal and power transmission.
Schleifring
Schleifring is a well-known manufacturer of electromechanical systems, including slip rings customized for various industries. Their Aircraft Slip Rings cater specifically to helicopters, offering robust performance, low wear, and high reliability to meet the challenges of aviation applications.
If you want to know more about other slip ring manufacturers, you can read Top 10 Slip Ring Manufacturers in China, Top 10 Slip Ring Manufacturers In the USA Market 2023, and Top 10 Slip Ring Industry Key Manufacturers 2023.
Future Trends of SMA Rotary Joints Technology
Discuss Where This Technology is Heading
With advancements in technology, SMA Rotary Joints are anticipated to evolve in both performance and application breadth. Key trends include:
- Miniaturization: As devices become smaller and more integrated, there’s a growing trend towards the miniaturization of all components, including rotary joints. Future rotary joints are expected to become even more compact without compromising their performance.
- Higher Frequency Capability: As applications require the transmission of data at even higher frequencies, the demand for SMA Rotary Joints capable of operating at these frequencies is expected to grow.
- Improved Durability: The quest for longer-lasting components remains a constant in engineering. Future rotary joints will likely be built with enhanced durability to reduce upkeep requirements and increase their operational lifespan.
- Smart and Self-Diagnostic Rotary Joints: With the rise of IoT and AI in the industrial sector, we could see the future incorporation of intelligent monitoring and self-diagnostic capabilities in rotary joints to alert maintenance teams about potential issues or failures.
The Potential Impact of These Trends
As these trends manifest, their impacts will also be felt across various domains:
- Expanded Applicability: The miniaturization and higher frequency compatibility will allow SMA Rotary Joints to be included in even more diverse applications than today, including emerging areas like IoT and 5G communication.
- Increased System Lifespan: With improved durability, systems that use SMA Rotary Joints will be able to function for longer periods without requiring significant maintenance, bringing in higher operational efficiency and cost savings.
- Automated Maintenance: The advent of smart rotary joints would transform the maintenance landscape, making it more predictive and thus reducing system downtime.
Altogether, these advancements in SMA Rotary Joint technology will bring about more robust and efficient systems, leading to significant enhancements in the sectors where they are employed, from communications to healthcare and beyond.
Conclusion
A comprehensive understanding of SMA Rotary Joints – their functioning, application, and selection criteria – is vital in this tech-forward era. As future trends pave the way for more advanced designs and applications, the relevance and importance of SMA Rotary Joints only seem to grow exponentially.
See What We Can Do

