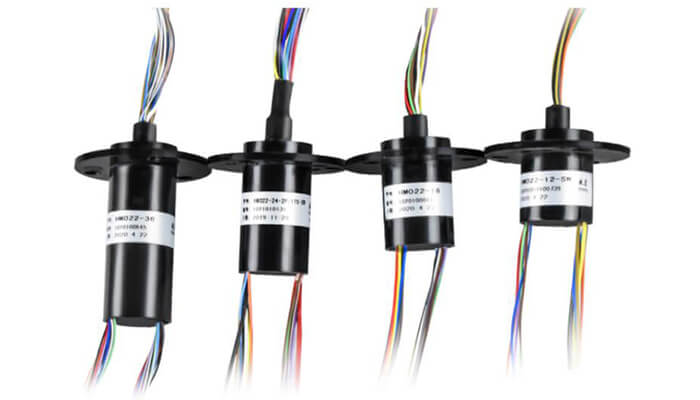
Slip rings are electrical components used in a variety of applications to enable the transfer of electrical power and signals between a stationary and a rotating structure. They are commonly used in wind turbines, cranes, and other rotating machinery.
However, slip rings are not without their drawbacks. One of the most common issues is electrical noise, which can interfere with the signals being transferred and lead to inaccurate readings. In this article, we’ll explore the causes of slip ring electrical noise and how it can be mitigated.
What Causes Slip Ring Electrical Noise?
Slip ring electrical noise is caused by a variety of factors, including the physical design of the slip rings, the materials used, and the environment in which they are operating. For example, the movement of the rings can cause friction, which can generate electrical noise. Additionally, the electrical components themselves can generate electrical noise due to their design or materials.
The environment in which the slip rings are operating can also play a role in the amount of electrical noise generated. For example, high temperatures or humid conditions can cause the materials used to expand or contract, leading to additional friction and noise.
Slip ring electrical noise can be caused by various factors that affect the stability and quality of the electrical connection between the rotating and stationary parts. Here are the primary causes:
Contact Resistance Variations
- Surface Roughness: Variations in the smoothness of the contact surfaces between the brushes and slip ring can lead to fluctuating contact resistance, causing electrical noise.
- Material Inhomogeneity: Differences in the material composition and properties of the slip ring and brushes can result in inconsistent contact resistance.
Wear and Tear
- Mechanical Wear: Over time, the mechanical friction between the brushes and slip ring surface can cause wear, leading to increased and inconsistent contact resistance.
- Brush Wear: As brushes wear down, their contact with the slip ring becomes less stable, contributing to noise.
Contamination
- Dust and Debris: Particles such as dust and debris can accumulate on the slip ring and brush surfaces, disrupting the contact and causing noise.
- Oxidation and Corrosion: Exposure to air and moisture can cause oxidation or corrosion on the slip ring surface, increasing resistance and noise.
Environmental Factors
- Temperature Fluctuations: Changes in temperature can cause expansion and contraction of materials, affecting the contact pressure and resistance.
- Humidity: High humidity can lead to moisture accumulation on the slip ring surfaces, causing oxidation or corrosion.
Electrical Issues
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): External electromagnetic fields can induce noise in the slip ring system.
- Signal Crosstalk: In systems with multiple electrical channels, signals can interfere with each other, causing noise.
Mechanical Factors
- Vibration: Mechanical vibrations from the rotating equipment can disrupt the contact between the brushes and slip ring, leading to noise.
- Misalignment: Misalignment of the slip ring assembly can cause uneven contact pressure and fluctuating resistance.
Design and Manufacturing Defects
- Poor Design: Inadequate design of the slip ring and brush system can result in poor contact and higher noise levels.
- Manufacturing Inconsistencies: Variations in manufacturing processes can lead to defects in the slip ring or brushes, affecting their performance and causing noise.
Practical Example
In a wind turbine, slip rings are used to transmit power and control signals from the stationary base to the rotating blades. If the slip ring surfaces become contaminated with dust or corroded due to exposure to the elements, the contact resistance can fluctuate, causing electrical noise. Regular maintenance and cleaning can help mitigate this issue.

Resistive noise in slip rings
Definition and Background
A slip ring is an electrical component used in rotary devices to transmit power and signals between a rotating part and a stationary part. It is commonly used in wind turbines, rotating antennas, radar systems, medical equipment, and more. During the operation of slip rings, resistive noise is a frequent issue that can affect device performance and signal integrity.
Sources of Resistive Noise
- Contact Resistance Variation: As the slip ring rotates, the contact between the brushes and the slip ring surface constantly changes. This variation in contact points can lead to fluctuations in contact resistance, generating resistive noise.
- Wear and Contamination: Wear and contamination (such as dust and grease) on the slip ring surface increase the instability of contact resistance, leading to resistive noise.
- Brush and Slip Ring Material: Different combinations of brush and slip ring materials have varying resistance characteristics. Mismatched materials can cause unstable contact resistance, producing resistive noise.

Manifestations of Resistive Noise
- Signal Distortion: Resistive noise can distort transmitted signals, particularly noticeable in high-frequency signal transmissions.
- Voltage Fluctuations: Variations in contact resistance can cause voltage output fluctuations, affecting power transmission stability.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Resistive noise can create electromagnetic interference, disrupting the normal operation of nearby electronic devices.
Measurement of Resistive Noise
Measuring resistive noise typically involves high-sensitivity noise measurement equipment. Common methods include:
- Spectrum Analysis: Using a spectrum analyzer to measure the frequency components of resistive noise.
- Time-Domain Analysis: Using an oscilloscope to observe the waveform and amplitude variations of resistive noise.
Control and Reduction of Resistive Noise
- Material Selection: Choosing high-quality, low-resistance brush and slip ring materials can significantly reduce resistive noise.
- Lubrication and Cleaning: Regular lubrication and cleaning of the slip ring surface reduce wear and the accumulation of contaminants.
- Design Optimization: Improving the design of slip rings and brushes to ensure smooth and uniform contact surfaces enhances contact stability.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular monitoring of the resistance changes in slip rings and timely maintenance and replacement of worn components.
Examples and Applications
In wind turbines, slip rings are used to transmit power and control signals. Resistive noise can affect the operational efficiency of the turbines and the accuracy of signal transmission. Therefore, wind turbine manufacturers pay special attention to the issue of resistive noise in slip rings, using high-quality materials, optimizing designs, and performing regular maintenance to minimize the impact of resistive noise on device performance.
Understanding and effectively controlling resistive noise can significantly improve the performance and reliability of slip ring systems, ensuring the stable operation of rotary equipment.
Resistive noise in slip rings is caused by the instability of contact resistance. By selecting appropriate materials, optimizing designs, and conducting regular maintenance, resistive noise can be effectively reduced, enhancing the performance and reliability of the equipment.
How Can Slip Ring Electrical Noise Be Mitigated?
The best way to reduce slip ring electrical noise is to use high-quality components and ensure that they are properly installed and maintained. For example, using slip rings made from materials that are resistant to friction and wear can help reduce noise. Additionally, installing the rings in a way that minimizes friction and vibration can help reduce noise.
Finally, it’s important to ensure that the environment in which the slip rings are operating is properly regulated. This includes ensuring that the temperature and humidity levels are within acceptable limits.
Slip ring electrical noise can be a major issue in many applications, but it can be mitigated with the right components and installation techniques. Additionally, ensuring that the environment in which the slip rings are operating is properly regulated can help reduce noise.
How to Deal with Slip Ring Electrical Noise
Dealing with slip ring electrical noise involves several strategies aimed at minimizing contact resistance variations and ensuring stable electrical connections. Here are some effective methods to address this issue:
Material Selection
- High-Quality Materials: Use high-quality, low-resistance materials for both the slip rings and brushes. Materials like gold, silver, or graphite are commonly used for their excellent conductivity and low noise characteristics.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure that the materials of the slip ring and brushes are compatible to reduce friction and wear, which can contribute to noise.
Design Optimization
- Contact Surface: Design slip rings with smooth and uniform contact surfaces to ensure consistent electrical connections.
- Multiple Contact Points: Use multiple contact points (multi-finger brushes) to maintain a stable connection even if one contact point fails, reducing noise.
- Spring-Loaded Brushes: Implement spring-loaded brushes to maintain consistent pressure and contact with the slip ring surface, reducing variations in contact resistance.
Maintenance and Cleaning
- Regular Cleaning: Periodically clean the slip ring and brush surfaces to remove dust, debris, and other contaminants that can cause noise.
- Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubricants to reduce friction and wear. Use conductive lubricants specifically designed for slip rings to maintain electrical conductivity.
- Inspection and Replacement: Regularly inspect the slip rings and brushes for signs of wear and replace them as necessary to ensure optimal performance.
Environmental Control
- Controlled Environment: Install slip rings in a controlled environment to minimize exposure to dust, moisture, and other contaminants.
- Sealing and Enclosures: Use sealed slip rings or enclosures to protect against environmental factors that can cause contamination and noise.
Electrical Filtering
- Filters: Install electrical filters (such as capacitors or inductors) in the circuitry to suppress electrical noise and prevent it from affecting the overall system performance.
- Shielding: Use shielding techniques to protect sensitive electronic components from electromagnetic interference caused by slip ring noise.
Monitoring and Diagnostics
- Noise Monitoring: Implement noise monitoring systems to continuously assess the level of electrical noise in the slip ring assembly.
- Predictive Maintenance: Use predictive maintenance techniques, such as vibration analysis and thermal imaging, to detect early signs of wear or failure, allowing for timely intervention.

Design and Installation Best Practices
- Cable Management: Properly manage and route cables to minimize electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, which can contribute to noise.
- Grounding: Ensure proper grounding of the slip ring assembly to reduce electrical noise and improve overall system stability.
Practical Example
In wind turbines, slip rings are crucial for transmitting power and control signals. To deal with electrical noise, wind turbine manufacturers might use gold-plated slip rings for their excellent conductivity and low noise characteristics. They also implement regular maintenance schedules to clean and inspect the slip rings and brushes, apply conductive lubricants, and use electrical filters to suppress noise.
Dealing with slip ring electrical noise requires a combination of high-quality materials, optimized design, regular maintenance, environmental control, electrical filtering, and proper installation practices. By implementing these strategies, you can significantly reduce electrical noise and improve the performance and reliability of slip ring systems.
See What We Can Do

